
Question Number 102341 by Ar Brandon last updated on 08/Jul/20
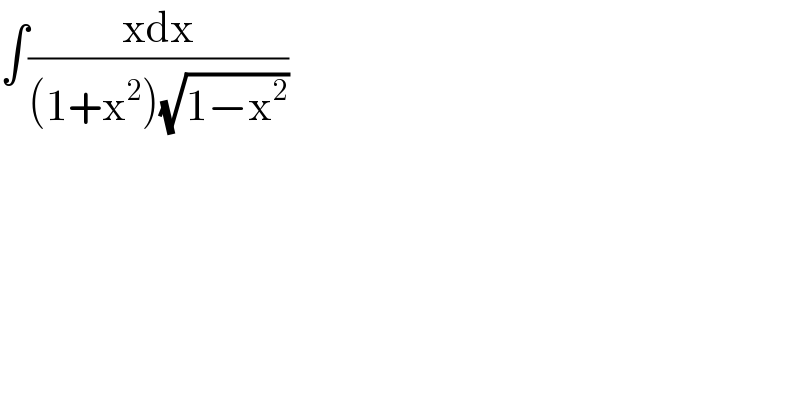
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{xdx}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 08/Jul/20
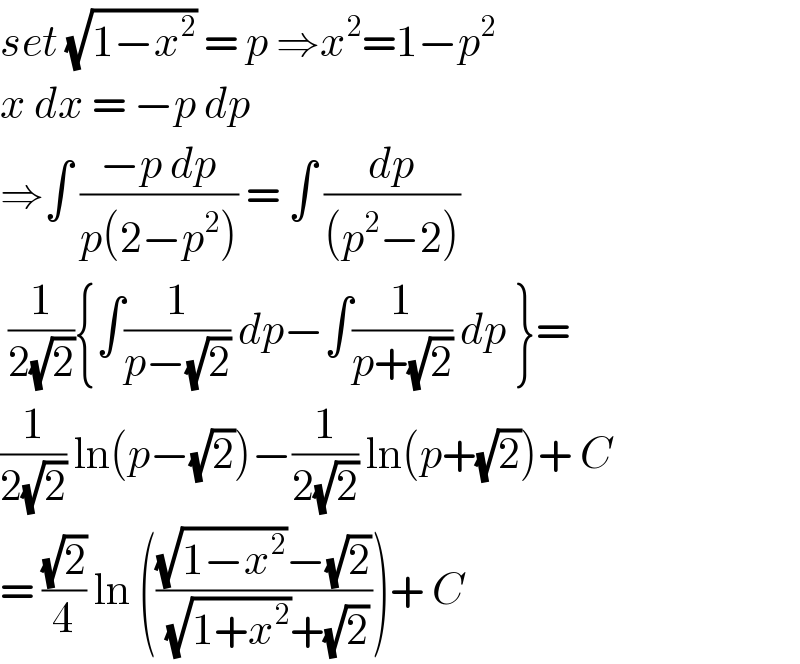
$${set}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:{p}\:\Rightarrow{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}−{p}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${x}\:{dx}\:=\:−{p}\:{dp} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\int\:\frac{−{p}\:{dp}}{{p}\left(\mathrm{2}−{p}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:=\:\int\:\frac{{dp}}{\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\left\{\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:{dp}−\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:{dp}\:\right\}= \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{ln}\left({p}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{ln}\left({p}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\:{C} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)+\:{C} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 08/Jul/20
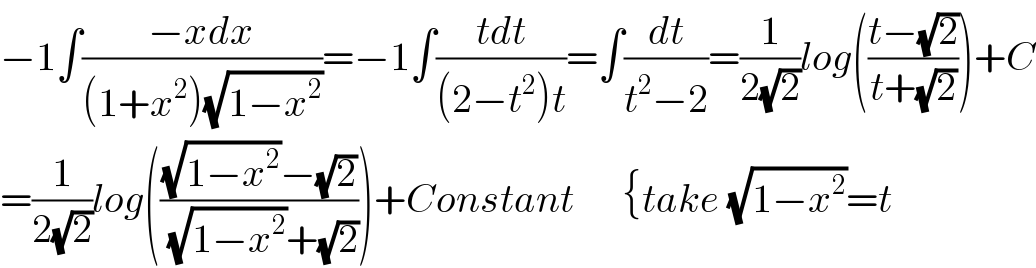
$$−\mathrm{1}\int\frac{−{xdx}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}=−\mathrm{1}\int\frac{{tdt}}{\left(\mathrm{2}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){t}}=\int\frac{{dt}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{log}\left(\frac{{t}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{{t}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)+{C} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{log}\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)+{Constant}\:\:\:\:\:\:\left\{{take}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }={t}\right. \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 08/Jul/20
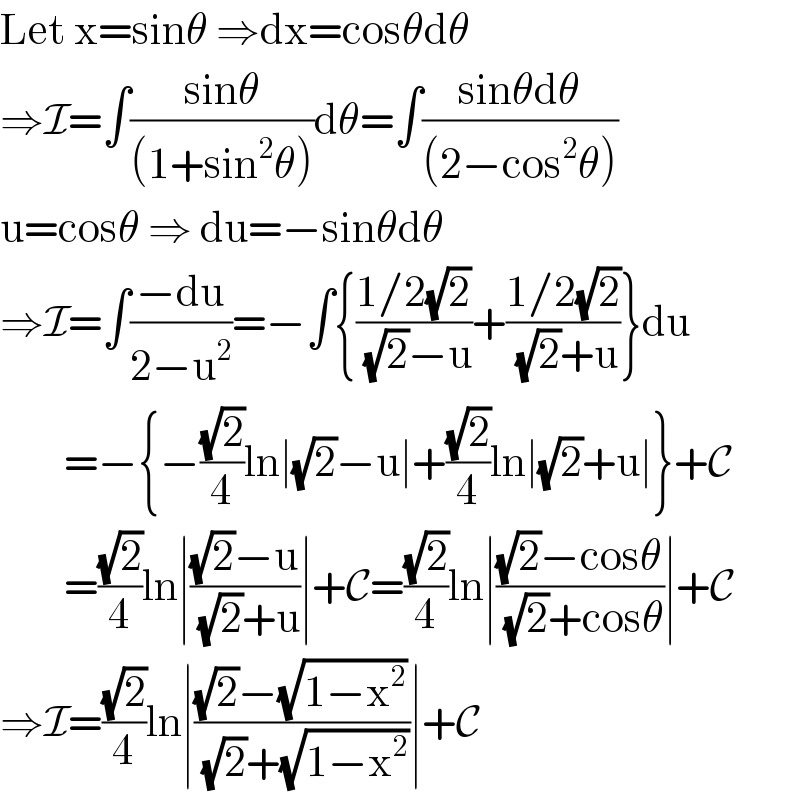
$$\mathrm{Let}\:\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{sin}\theta\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{cos}\theta\mathrm{d}\theta \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathcal{I}=\int\frac{\mathrm{sin}\theta}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta\right)}\mathrm{d}\theta=\int\frac{\mathrm{sin}\theta\mathrm{d}\theta}{\left(\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta\right)} \\ $$$$\mathrm{u}=\mathrm{cos}\theta\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{du}=−\mathrm{sin}\theta\mathrm{d}\theta \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathcal{I}=\int\frac{−\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }=−\int\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{u}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{u}}\right\}\mathrm{du} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\left\{−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{u}\mid+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{u}\mid\right\}+\mathcal{C} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{u}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{u}}\mid+\mathcal{C}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{cos}\theta}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{cos}\theta}\mid+\mathcal{C} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathcal{I}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\mid+\mathcal{C} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 08/Jul/20
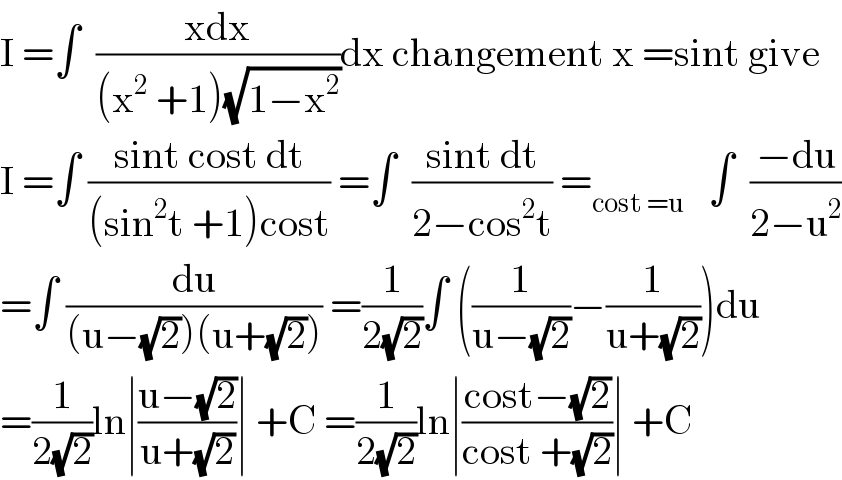
$$\mathrm{I}\:=\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{xdx}}{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\mathrm{dx}\:\mathrm{changement}\:\mathrm{x}\:=\mathrm{sint}\:\mathrm{give} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\int\:\frac{\mathrm{sint}\:\mathrm{cost}\:\mathrm{dt}}{\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{t}\:+\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{cost}}\:=\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{sint}\:\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{t}}\:=_{\mathrm{cost}\:=\mathrm{u}} \:\:\:\int\:\:\frac{−\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\int\:\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\left(\mathrm{u}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\left(\mathrm{u}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{u}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{u}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)\mathrm{du} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\mathrm{u}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{u}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mid\:+\mathrm{C}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\mathrm{cost}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{cost}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mid\:+\mathrm{C} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 08/Jul/20
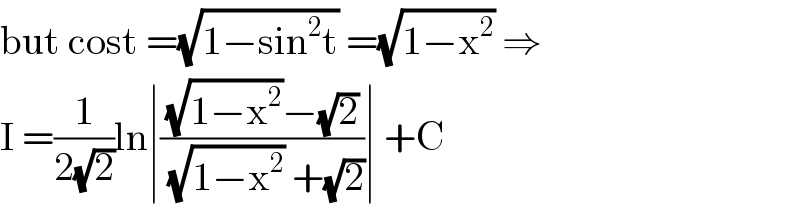
$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{cost}\:=\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{t}}\:=\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mid\:+\mathrm{C} \\ $$
