
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 114978 by srijachakraborty last updated on 22/Sep/20
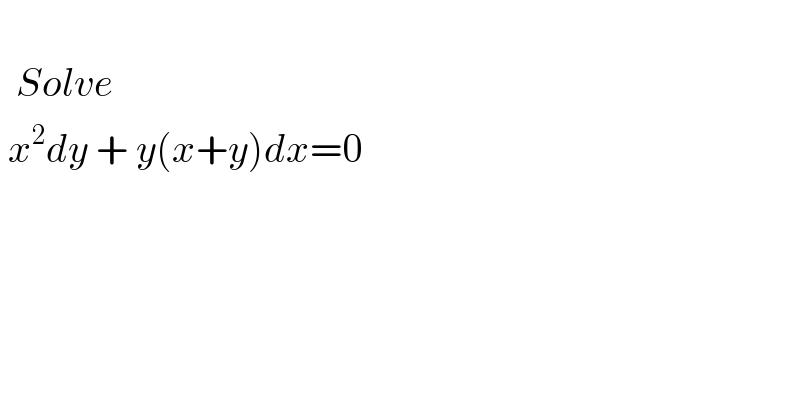
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:{Solve}\: \\ $$$$\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {dy}\:+\:{y}\left({x}+{y}\right){dx}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by soumyasaha last updated on 22/Sep/20

Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 22/Sep/20
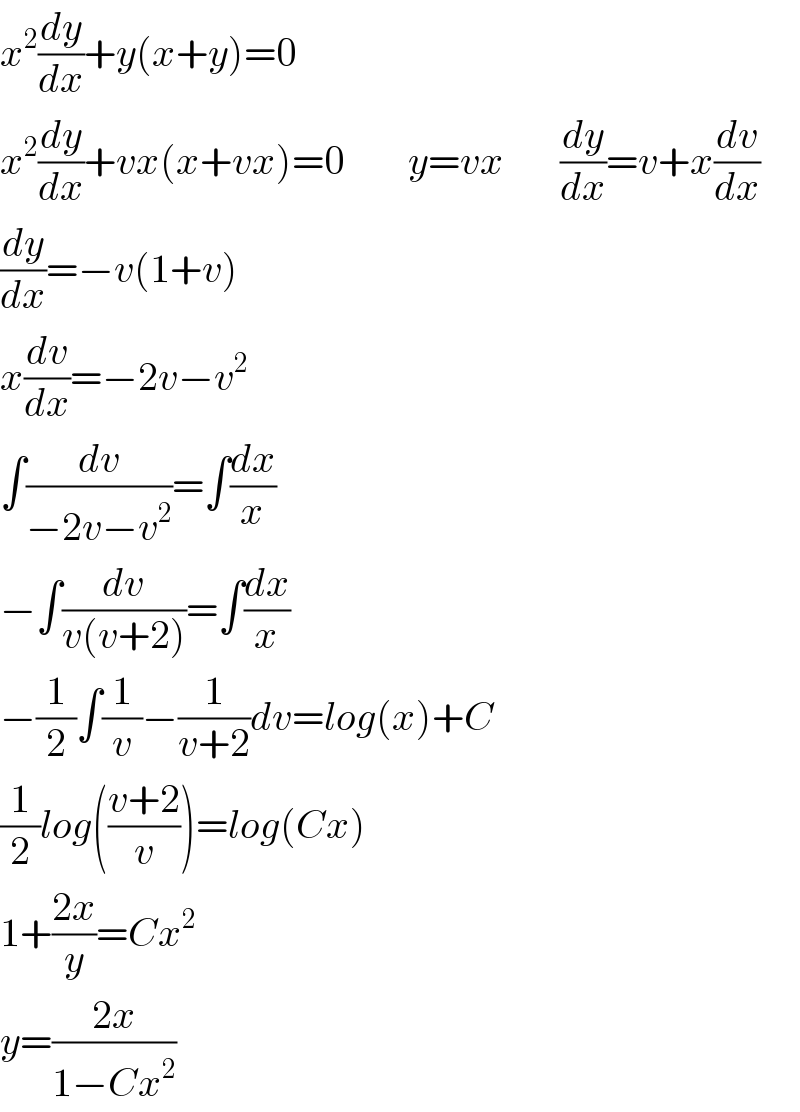
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{dy}}{{dx}}+{y}\left({x}+{y}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{dy}}{{dx}}+{vx}\left({x}+{vx}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{y}={vx}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}={v}+{x}\frac{{dv}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=−{v}\left(\mathrm{1}+{v}\right)\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$${x}\frac{{dv}}{{dx}}=−\mathrm{2}{v}−{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\int\frac{{dv}}{−\mathrm{2}{v}−{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$−\int\frac{{dv}}{{v}\left({v}+\mathrm{2}\right)}=\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{v}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{v}+\mathrm{2}}{dv}={log}\left({x}\right)+{C} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{log}\left(\frac{{v}+\mathrm{2}}{{v}}\right)={log}\left({Cx}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{{y}}={Cx}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{1}−{Cx}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by srijachakraborty last updated on 22/Sep/20
thank you sir
