
Question Number 118193 by mathocean1 last updated on 15/Oct/20
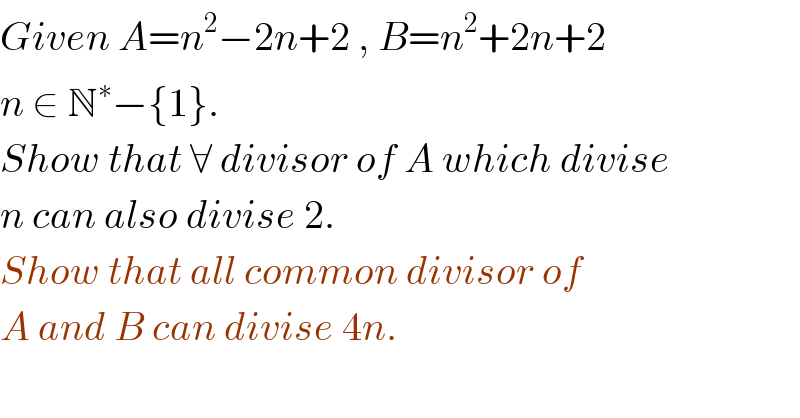
$${Given}\:{A}={n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\:,\:{B}={n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${n}\:\in\:\mathbb{N}^{\ast} −\left\{\mathrm{1}\right\}. \\ $$$${Show}\:{that}\:\forall\:{divisor}\:{of}\:{A}\:{which}\:{divise} \\ $$$${n}\:{can}\:{also}\:{divise}\:\mathrm{2}. \\ $$$${Show}\:{that}\:{all}\:{common}\:{divisor}\:{of}\: \\ $$$${A}\:{and}\:{B}\:{can}\:{divise}\:\mathrm{4}{n}. \\ $$
Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 16/Oct/20
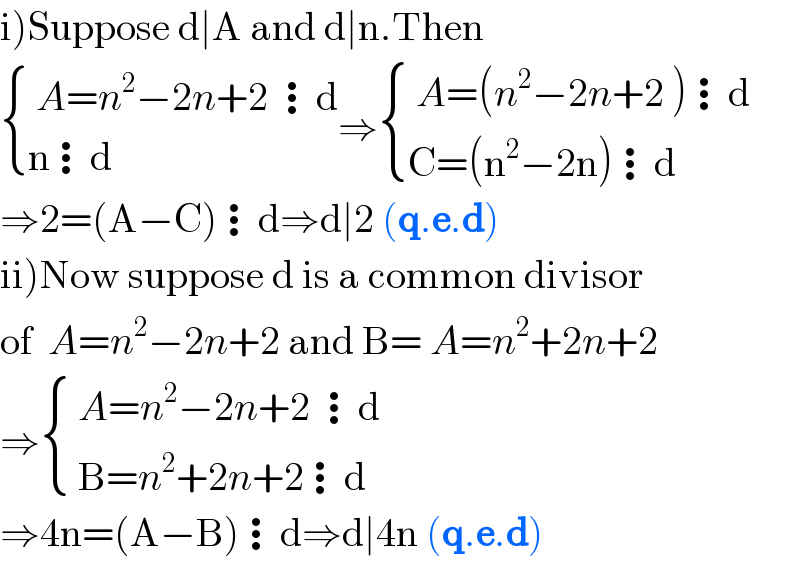
$$\left.\mathrm{i}\right)\mathrm{Suppose}\:\mathrm{d}\mid\mathrm{A}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{d}\mid\mathrm{n}.\mathrm{Then} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\:{A}={n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\:\vdots\mathrm{d}}\\{\mathrm{n}\vdots\mathrm{d}}\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\:{A}=\left({n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\:\right)\vdots\mathrm{d}}\\{\mathrm{C}=\left(\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2n}\right)\vdots\mathrm{d}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}=\left(\mathrm{A}−\mathrm{C}\right)\vdots\mathrm{d}\Rightarrow\mathrm{d}\mid\mathrm{2}\:\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{q}}.\boldsymbol{\mathrm{e}}.\boldsymbol{\mathrm{d}}\right)\: \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{ii}\right)\mathrm{Now}\:\mathrm{suppose}\:\mathrm{d}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{common}\:\mathrm{divisor} \\ $$$$\mathrm{of}\:\:{A}={n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{B}=\:{A}={n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\:{A}={n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\:\vdots\mathrm{d}}\\{\:\mathrm{B}={n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\vdots\mathrm{d}\:}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{4n}=\left(\mathrm{A}−\mathrm{B}\right)\vdots\mathrm{d}\Rightarrow\mathrm{d}\mid\mathrm{4n}\:\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{q}}.\boldsymbol{\mathrm{e}}.\boldsymbol{\mathrm{d}}\right) \\ $$
