
Question Number 143329 by Huy last updated on 13/Jun/21
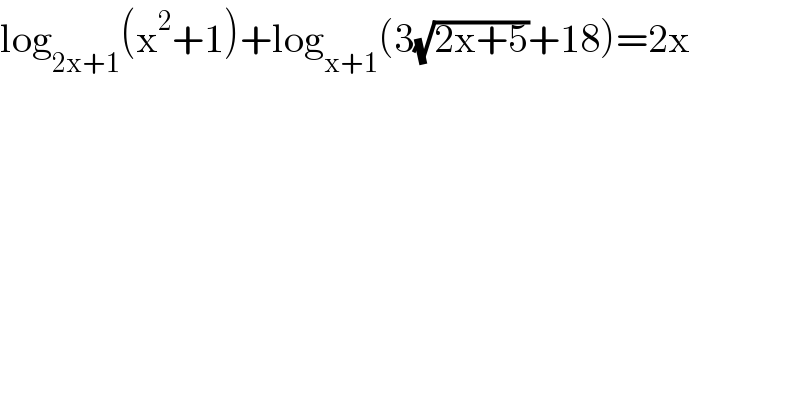
$$\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{18}\right)=\mathrm{2x} \\ $$
Answered by Olaf_Thorendsen last updated on 13/Jun/21
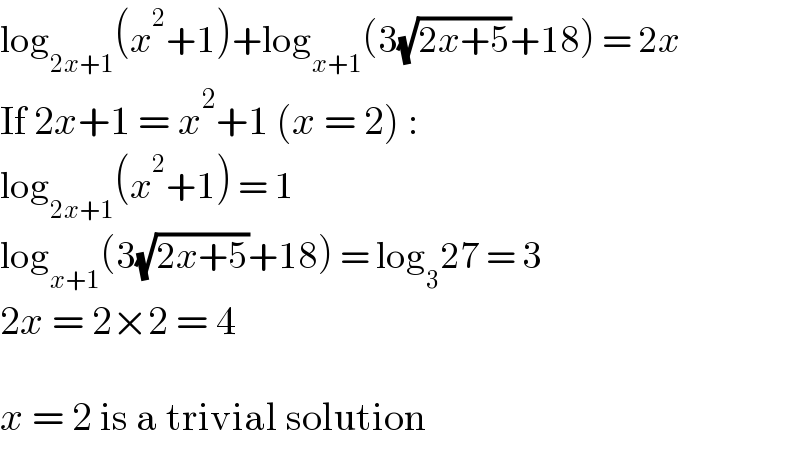
$$\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} \left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{log}_{{x}+\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{18}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{If}\:\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\:=\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\:\left({x}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\right)\:: \\ $$$$\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} \left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{log}_{{x}+\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{18}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{27}\:=\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}\:=\:\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${x}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{trivial}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$
