
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 148303 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 26/Jul/21
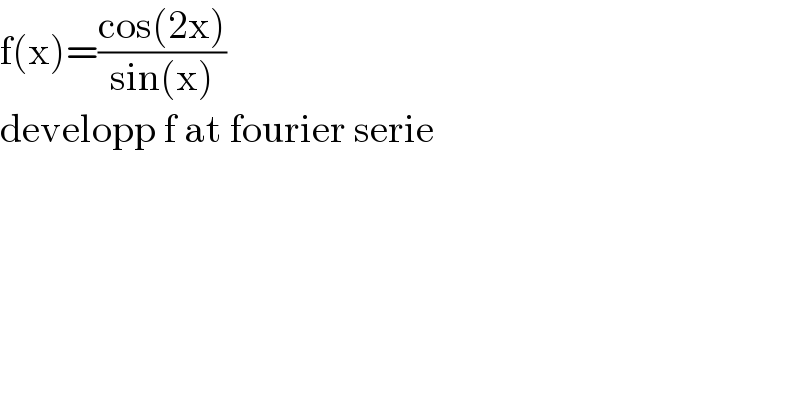
$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)}{\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} \\ $$$$\mathrm{developp}\:\mathrm{f}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{fourier}\:\mathrm{serie} \\ $$
Answered by Olaf_Thorendsen last updated on 27/Jul/21

$${f}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{sin}{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:=\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\mathrm{cos}\left(\left(\mathrm{2}{nx}\right)−\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}\right)\right.\right. \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{telescopic}\:\mathrm{sum}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:=\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\mathrm{cos}\left(\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}−{x}\right)−\mathrm{cos}\left(\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}+{x}\right)\right. \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{2}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{cos}\left(\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}−{x}\right)−\mathrm{cos}\left(\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}+{x}\right)\right. \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{2}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{sin}\left(\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}\right).\mathrm{sin}{x} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{sin}{x}}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{sin}\left(\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{0}} \:=\:\mathrm{0}\:{and}\:\forall{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1},\:{a}_{{n}} \:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{because}\:{f}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{odd}\right) \\ $$$$\:\forall{n}\in\mathbb{N}^{\ast} ,\:{b}_{\mathrm{2}{n}} \:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{and}\:\forall{n}\in\mathbb{N},\:{b}_{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 27/Jul/21
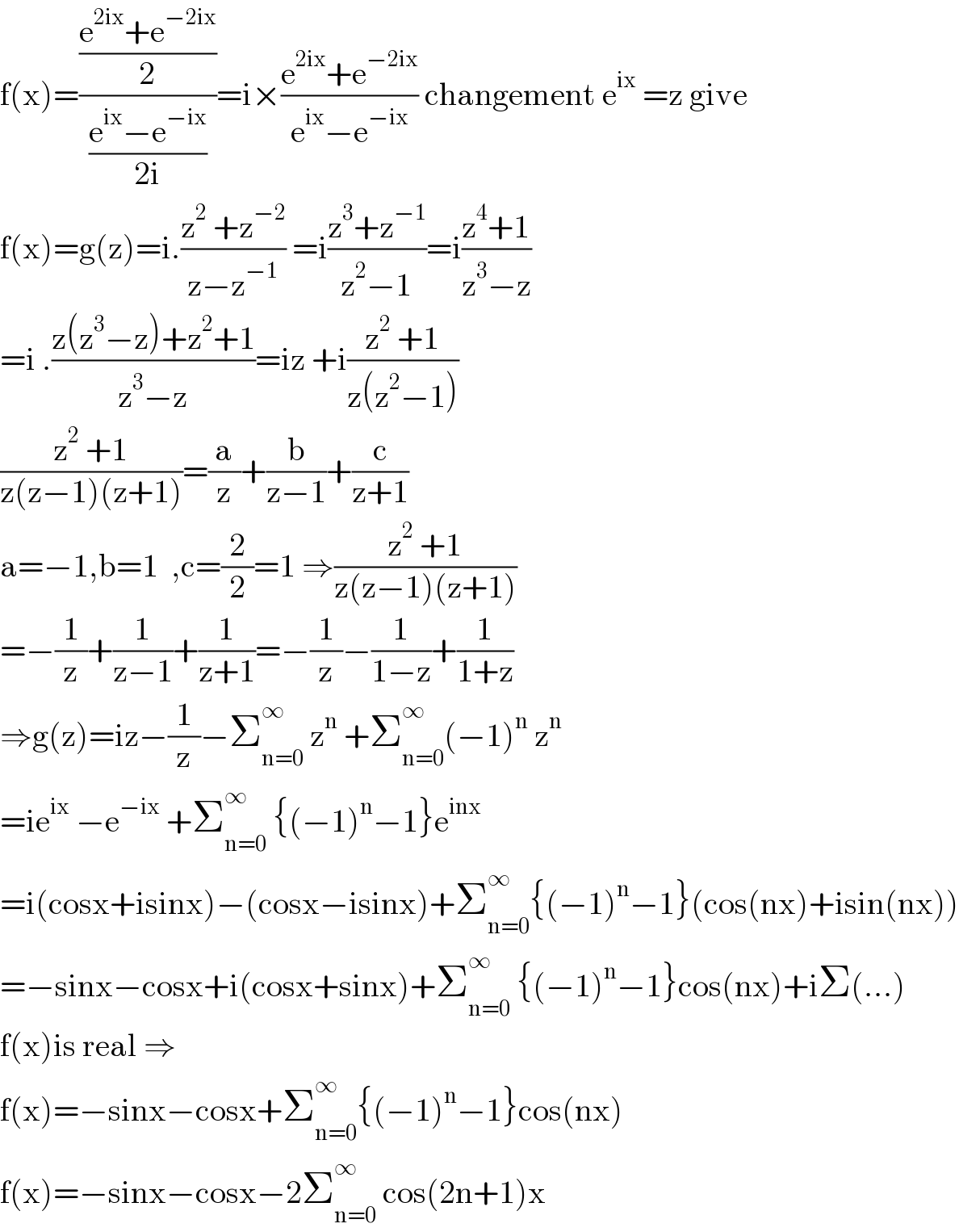
$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2ix}} +\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2ix}} }{\mathrm{2}}}{\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{ix}} −\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{ix}} }{\mathrm{2i}}}=\mathrm{i}×\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2ix}} +\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2ix}} }{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{ix}} −\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{ix}} }\:\mathrm{changement}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{ix}} \:=\mathrm{z}\:\mathrm{give} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{g}\left(\mathrm{z}\right)=\mathrm{i}.\frac{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{z}^{−\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{z}^{−\mathrm{1}} }\:=\mathrm{i}\frac{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{z}^{−\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{i}\frac{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{z}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{i}\:.\frac{\mathrm{z}\left(\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{z}\right)+\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{z}}=\mathrm{iz}\:+\mathrm{i}\frac{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}\left(\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}\left(\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{z}}+\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}=−\mathrm{1},\mathrm{b}=\mathrm{1}\:\:,\mathrm{c}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}\left(\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{1}}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{z}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{z}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{g}\left(\mathrm{z}\right)=\mathrm{iz}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{z}}−\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{n}} \:+\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} \:\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{n}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ie}^{\mathrm{ix}} \:−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{ix}} \:+\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\left\{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{1}\right\}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{inx}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{i}\left(\mathrm{cosx}+\mathrm{isinx}\right)−\left(\mathrm{cosx}−\mathrm{isinx}\right)+\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left\{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{1}\right\}\left(\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{nx}\right)+\mathrm{isin}\left(\mathrm{nx}\right)\right) \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{sinx}−\mathrm{cosx}+\mathrm{i}\left(\mathrm{cosx}+\mathrm{sinx}\right)+\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\left\{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{1}\right\}\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{nx}\right)+\mathrm{i}\Sigma\left(...\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{real}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=−\mathrm{sinx}−\mathrm{cosx}+\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left\{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{1}\right\}\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{nx}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=−\mathrm{sinx}−\mathrm{cosx}−\mathrm{2}\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{2n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{x} \\ $$
