
Question Number 148992 by mathlove last updated on 02/Aug/21
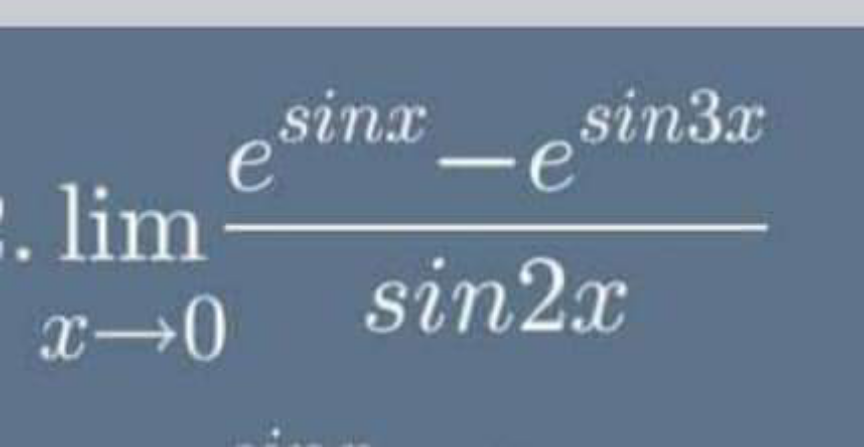
Answered by gsk2684 last updated on 02/Aug/21
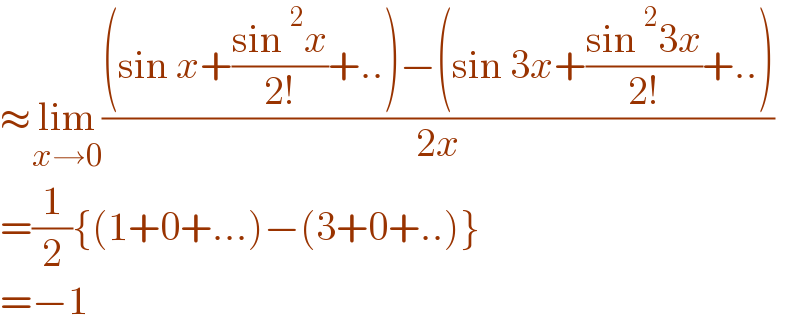
$$\approx\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{\mathrm{2}!}+..\right)−\left(\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{3}{x}}{\mathrm{2}!}+..\right)}{\mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left\{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{0}+...\right)−\left(\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{0}+..\right)\right\} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by iloveisrael last updated on 02/Aug/21
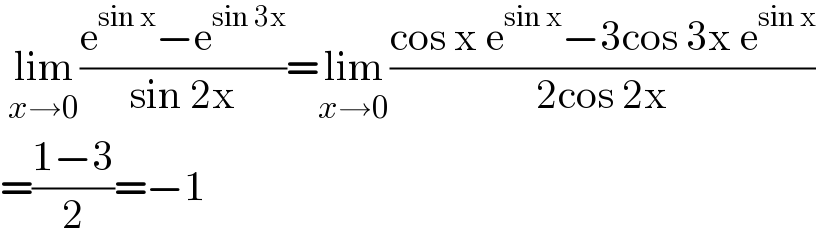
$$\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}} −\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3x}} }{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2x}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}} −\mathrm{3cos}\:\mathrm{3x}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2cos}\:\mathrm{2x}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
