
Question Number 149339 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 04/Aug/21
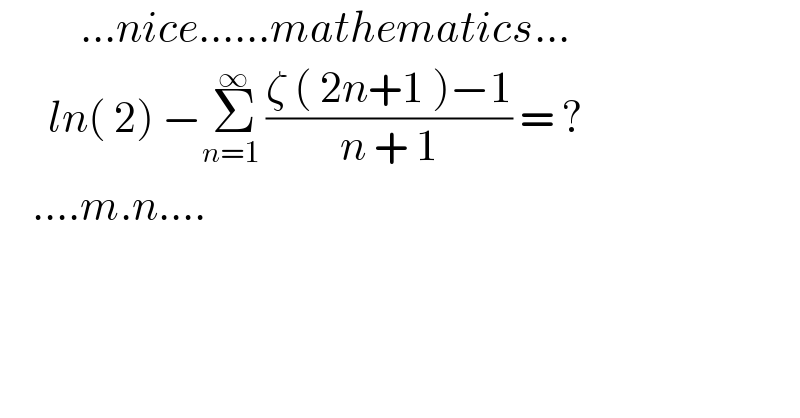
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:...{nice}......{mathematics}... \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:{ln}\left(\:\mathrm{2}\right)\:−\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}\:} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\zeta\:\left(\:\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\:\right)−\mathrm{1}}{{n}\:+\:\mathrm{1}}\:=\:? \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:....{m}.{n}.... \\ $$
Answered by Kamel last updated on 04/Aug/21
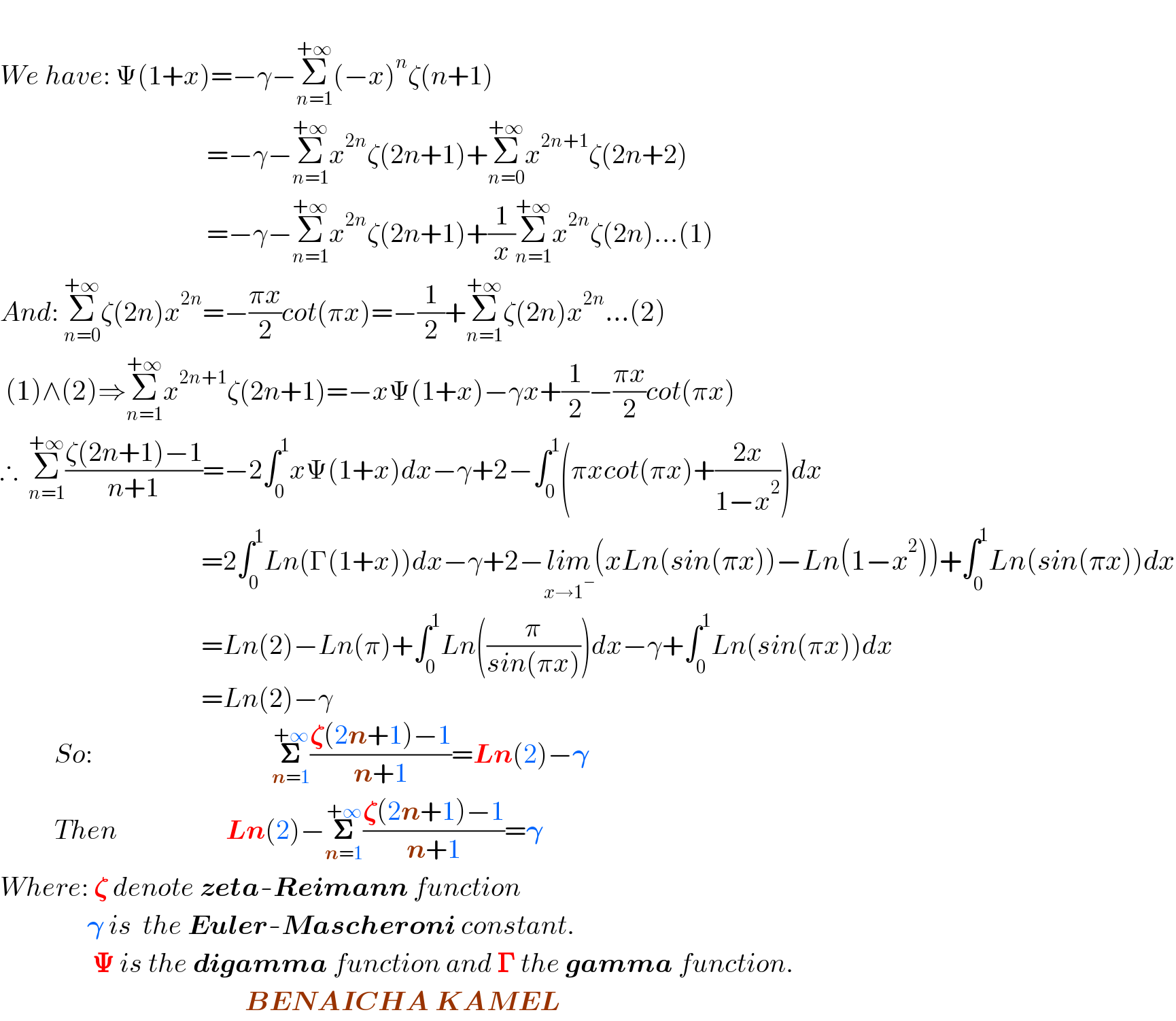
$$ \\ $$$${We}\:{have}:\:\Psi\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)=−\gamma−\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\left(−{x}\right)^{{n}} \zeta\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\gamma−\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} \zeta\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \zeta\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\gamma−\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} \zeta\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} \zeta\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)...\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${And}:\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\zeta\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} =−\frac{\pi{x}}{\mathrm{2}}{cot}\left(\pi{x}\right)=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\zeta\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} ...\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\wedge\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\Rightarrow\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \zeta\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)=−{x}\Psi\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)−\gamma{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\pi{x}}{\mathrm{2}}{cot}\left(\pi{x}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\zeta\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{{n}+\mathrm{1}}=−\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {x}\Psi\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right){dx}−\gamma+\mathrm{2}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \left(\pi{xcot}\left(\pi{x}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}\left(\Gamma\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\right){dx}−\gamma+\mathrm{2}−\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}^{−} } {{lim}}\left({xLn}\left({sin}\left(\pi{x}\right)\right)−{Ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right)+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}\left({sin}\left(\pi{x}\right)\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:={Ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−{Ln}\left(\pi\right)+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}\left(\frac{\pi}{{sin}\left(\pi{x}\right)}\right){dx}−\gamma+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}\left({sin}\left(\pi{x}\right)\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:={Ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\gamma \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{So}:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\underset{\boldsymbol{{n}}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\boldsymbol{\sum}}}\frac{\boldsymbol{\zeta}\left(\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}}=\boldsymbol{{Ln}}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\boldsymbol{\gamma} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{Then}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{Ln}}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\underset{\boldsymbol{{n}}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{+\infty} {\boldsymbol{\sum}}}\frac{\boldsymbol{\zeta}\left(\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{n}}+\mathrm{1}}=\boldsymbol{\gamma} \\ $$$${Where}:\:\boldsymbol{\zeta}\:{denote}\:\boldsymbol{{zeta}}-\boldsymbol{{Reimann}}\:{function} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\gamma}\:{is}\:\:{the}\:\boldsymbol{{Euler}}-\boldsymbol{{Mascheroni}}\:{constant}. \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\Psi}\:{is}\:{the}\:\boldsymbol{{digamma}}\:{function}\:{and}\:\boldsymbol{\Gamma}\:{the}\:\boldsymbol{{gamma}}\:{function}. \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{BENAICHA}}\:\boldsymbol{{KAMEL}} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 04/Aug/21
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{very}\:{nice}\:{master}\:,\:\:\mathrm{M}{r}\:.\mathrm{K}{amel}.. \\ $$
Commented by Kamel last updated on 04/Aug/21

$${Thank}\:{you}. \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 04/Aug/21

$$\mathrm{Weldone}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
