
Question Number 169549 by ali009 last updated on 02/May/22
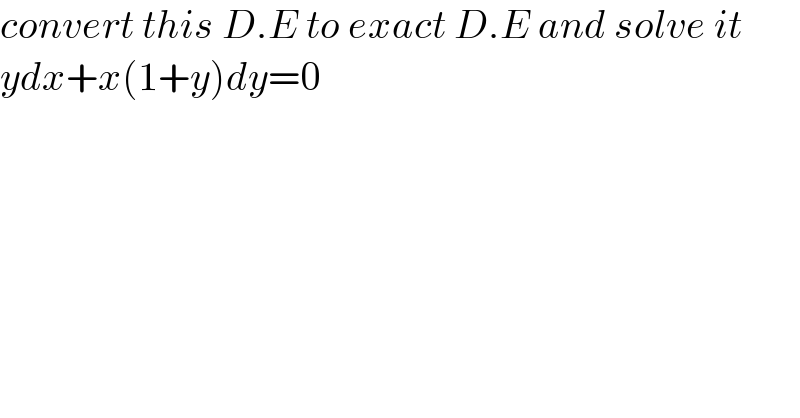
$${convert}\:{this}\:{D}.{E}\:{to}\:{exact}\:{D}.{E}\:{and}\:{solve}\:{it} \\ $$$${ydx}+{x}\left(\mathrm{1}+{y}\right){dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 02/May/22
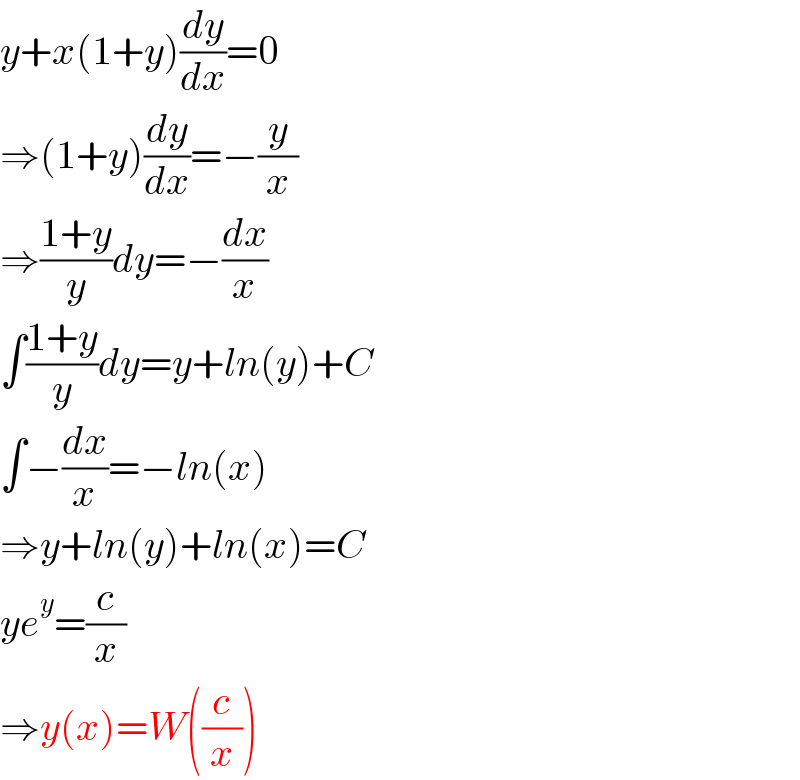
$${y}+{x}\left(\mathrm{1}+{y}\right)\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{1}+{y}\right)\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=−\frac{{y}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}+{y}}{{y}}{dy}=−\frac{{dx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}+{y}}{{y}}{dy}={y}+{ln}\left({y}\right)+{C} \\ $$$$\int−\frac{{dx}}{{x}}=−{ln}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}+{ln}\left({y}\right)+{ln}\left({x}\right)={C} \\ $$$${ye}^{{y}} =\frac{{c}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}\left({x}\right)={W}\left(\frac{{c}}{{x}}\right) \\ $$
Commented by ali009 last updated on 02/May/22

$${well}\:{done} \\ $$
