
Question Number 187531 by sciencestudentW last updated on 18/Feb/23
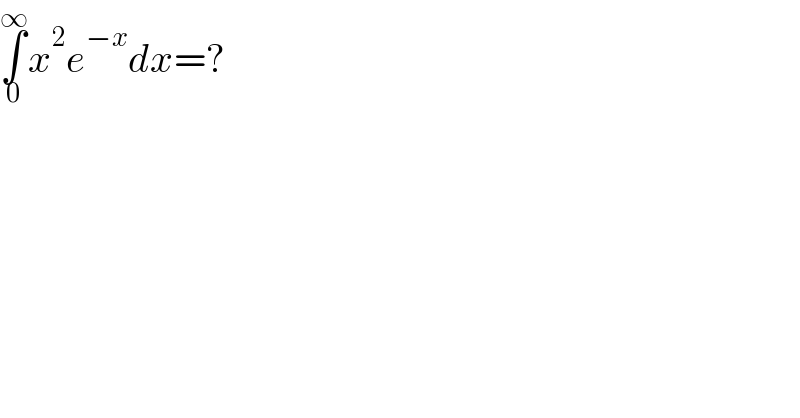
$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} {dx}=? \\ $$
Answered by a.lgnaoui last updated on 18/Feb/23
![posons t=e^x x=lnt dx=(dt/t) x^2 e^(−x) =(lnt)^2 ×(1/t)=((lnt)/t)×lnt ∫_0 ^∞ x^2 e^(−x) dx=∫_1 ^∞ [((1/2)lnt)^2 ]′lnt U=(1/2)[lnt]^2 V=lnt V^′ =(1/t) I=(1/2)(lnt)^2 −(1/2)∫((lnt)^2 )/t)dt=(1/2)(lnt)^3 ]_1 ^∞ −J 2I=(1/2)[(lnt)^2 ]_1 ^∞ ⇒ I=+∞](Q187550.png)
$${posons}\:\:\:{t}={e}^{{x}} \:\:{x}={lnt}\:\:\:{dx}=\frac{{dt}}{{t}} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} =\left({lnt}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}=\frac{{lnt}}{{t}}×{lnt} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} {dx}=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \left[\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{lnt}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right]'{lnt} \\ $$$${U}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[{lnt}\right]^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:\:\:{V}={lnt}\:\:\:\:\:{V}^{'} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}} \\ $$$$\left.{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({lnt}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{\left.{lnt}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{{t}}{dt}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({lnt}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \right]_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} −{J} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{I}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\left({lnt}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right]_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \Rightarrow\:{I}=+\infty \\ $$
Answered by ARUNG_Brandon_MBU last updated on 18/Feb/23
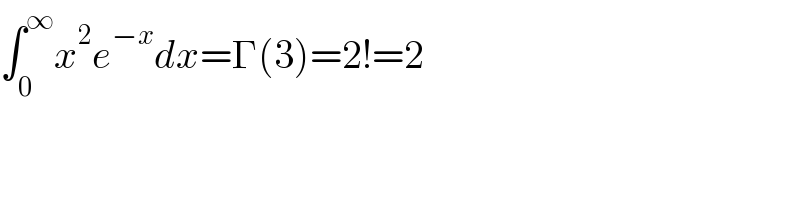
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} {dx}=\Gamma\left(\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{2}!=\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Answered by ARUNG_Brandon_MBU last updated on 18/Feb/23
![I=∫_0 ^∞ x^2 e^(−x) dx { ((u(x)=x^2 )),((v′(x)=e^(−x) )) :}⇒ { ((u′(x)=2x)),((v(x)=−e^(−x) )) :} I=[−x^2 e^(−x) ]_0 ^∞ +2∫_0 ^∞ xe^(−x) dx =2∫_0 ^∞ xe^(−x) dx=2[−xe^(−x) ]_0 ^∞ +2∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x) dx =2∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x) dx=2[−e^(−x) ]_0 ^∞ =2](Q187564.png)
$${I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\mathrm{u}\left({x}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\\{\mathrm{v}'\left({x}\right)={e}^{−{x}} }\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\mathrm{u}'\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}}\\{\mathrm{v}\left({x}\right)=−{e}^{−{x}} }\end{cases} \\ $$$${I}=\left[−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} +\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xe}^{−{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$\:\:=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {xe}^{−{x}} {dx}=\mathrm{2}\left[−{xe}^{−{x}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} +\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$\:\:=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{x}} {dx}=\mathrm{2}\left[−{e}^{−{x}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} =\mathrm{2} \\ $$
