
Question Number 31952 by 24444355 last updated on 17/Mar/18
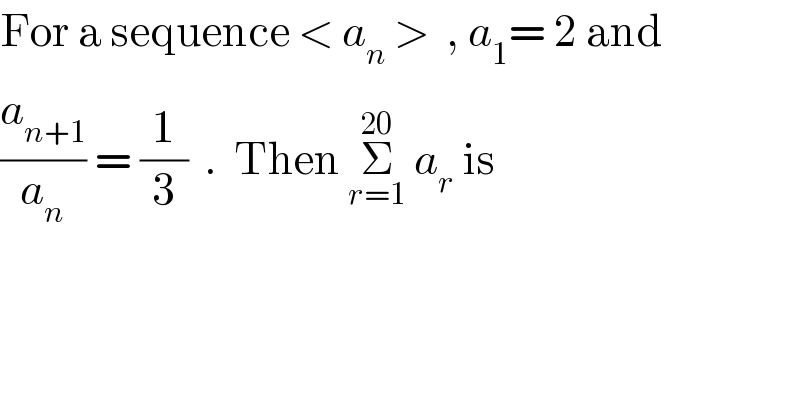
$$\mathrm{For}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{sequence}\:<\:{a}_{{n}} \:>\:\:,\:{a}_{\mathrm{1}} =\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{and}\: \\ $$ $$\frac{{a}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{{a}_{{n}} }\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\:.\:\:\mathrm{Then}\:\underset{{r}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{20}} {\sum}}\:{a}_{{r}} \:\mathrm{is} \\ $$
Commented byabdo imad last updated on 17/Mar/18
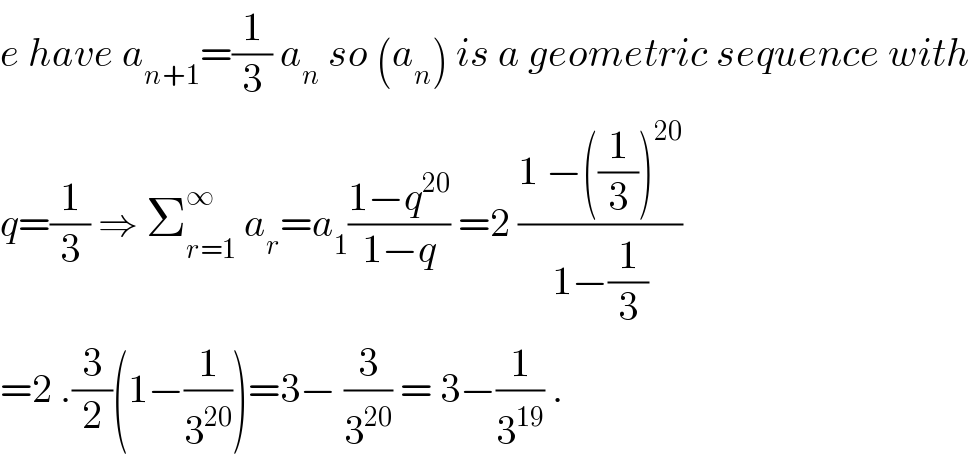
$${e}\:{have}\:{a}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:{a}_{{n}} \:{so}\:\left({a}_{{n}} \right)\:{is}\:{a}\:{geometric}\:{sequence}\:{with} \\ $$ $${q}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\Rightarrow\:\sum_{{r}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:{a}_{{r}} ={a}_{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}−{q}^{\mathrm{20}} }{\mathrm{1}−{q}}\:=\mathrm{2}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}\:−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{20}} }{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$ $$=\mathrm{2}\:.\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{20}} }\right)=\mathrm{3}−\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{20}} }\:=\:\mathrm{3}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{19}} }\:. \\ $$
