
Question Number 3886 by 123456 last updated on 23/Dec/15
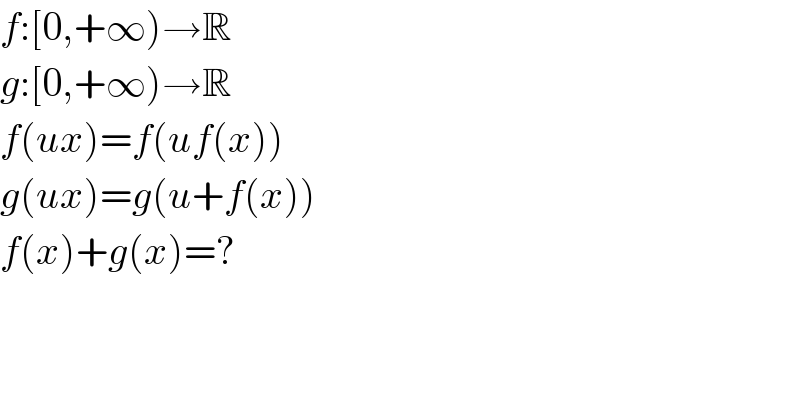
$${f}:\left[\mathrm{0},+\infty\right)\rightarrow\mathbb{R} \\ $$$${g}:\left[\mathrm{0},+\infty\right)\rightarrow\mathbb{R} \\ $$$${f}\left({ux}\right)={f}\left({uf}\left({x}\right)\right) \\ $$$${g}\left({ux}\right)={g}\left({u}+{f}\left({x}\right)\right) \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)+{g}\left({x}\right)=? \\ $$
Commented by Yozzii last updated on 24/Dec/15
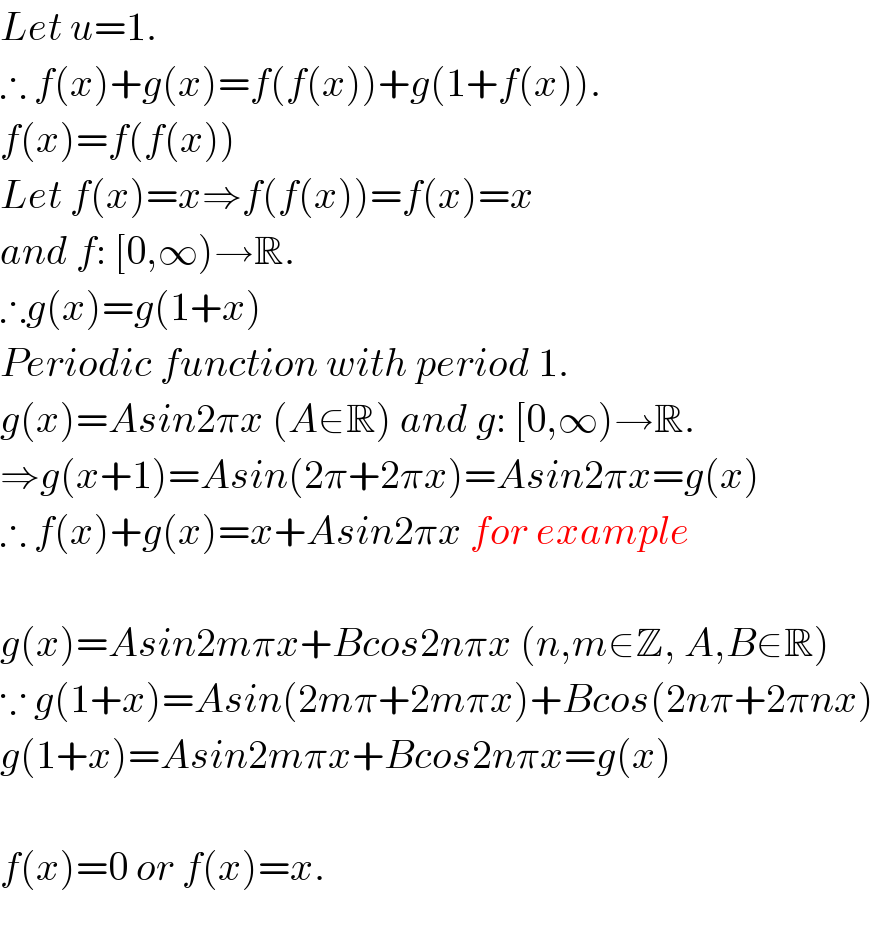
$${Let}\:{u}=\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$$\therefore\:{f}\left({x}\right)+{g}\left({x}\right)={f}\left({f}\left({x}\right)\right)+{g}\left(\mathrm{1}+{f}\left({x}\right)\right). \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={f}\left({f}\left({x}\right)\right) \\ $$$${Let}\:{f}\left({x}\right)={x}\Rightarrow{f}\left({f}\left({x}\right)\right)={f}\left({x}\right)={x} \\ $$$${and}\:{f}:\:\left[\mathrm{0},\infty\right)\rightarrow\mathbb{R}. \\ $$$$\therefore{g}\left({x}\right)={g}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right) \\ $$$${Periodic}\:{function}\:{with}\:{period}\:\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)={Asin}\mathrm{2}\pi{x}\:\left({A}\in\mathbb{R}\right)\:{and}\:{g}:\:\left[\mathrm{0},\infty\right)\rightarrow\mathbb{R}. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{g}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)={Asin}\left(\mathrm{2}\pi+\mathrm{2}\pi{x}\right)={Asin}\mathrm{2}\pi{x}={g}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:{f}\left({x}\right)+{g}\left({x}\right)={x}+{Asin}\mathrm{2}\pi{x}\:{for}\:{example} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)={Asin}\mathrm{2}{m}\pi{x}+{Bcos}\mathrm{2}{n}\pi{x}\:\left({n},{m}\in\mathbb{Z},\:{A},{B}\in\mathbb{R}\right) \\ $$$$\because\:{g}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)={Asin}\left(\mathrm{2}{m}\pi+\mathrm{2}{m}\pi{x}\right)+{Bcos}\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\pi+\mathrm{2}\pi{nx}\right) \\ $$$${g}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)={Asin}\mathrm{2}{m}\pi{x}+{Bcos}\mathrm{2}{n}\pi{x}={g}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:{or}\:{f}\left({x}\right)={x}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
