
Question Number 53556 by 0955083339 last updated on 23/Jan/19
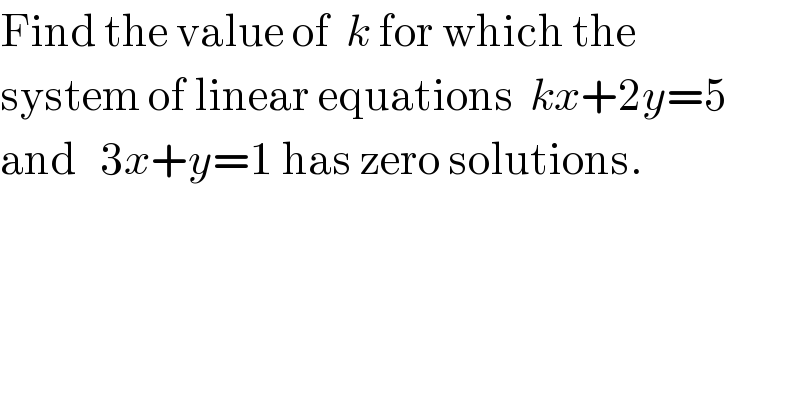
$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{of}\:\:{k}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{system}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{linear}\:\mathrm{equations}\:\:{kx}+\mathrm{2}{y}=\mathrm{5}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\:\:\mathrm{3}{x}+{y}=\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{zero}\:\mathrm{solutions}. \\ $$
Commented by Kunal12588 last updated on 23/Jan/19
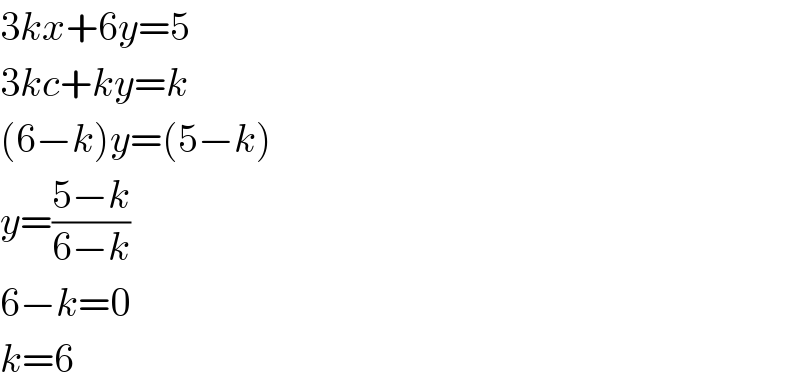
$$\mathrm{3}{kx}+\mathrm{6}{y}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{kc}+{ky}={k} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{6}−{k}\right){y}=\left(\mathrm{5}−{k}\right) \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{5}−{k}}{\mathrm{6}−{k}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{6}−{k}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${k}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$
Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 23/Jan/19

$${when}\:{the}\:{lines}\:{become}\:{parallel}\:{they}\:{have}\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${solutions}. \\ $$$${general}\:{solution}: \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{1}} {x}+{b}_{\mathrm{1}} {y}={c}_{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{2}} {x}+{b}_{\mathrm{2}} {y}={c}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${when}\:\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{a}_{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{b}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{b}_{\mathrm{2}} }\neq\frac{{c}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{c}_{\mathrm{2}} }\:{the}\:{lines}\:{were}\:{parallel} \\ $$$${given}\:{eq}^{{n}} {s} \\ $$$${kx}+\mathrm{2}{y}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{x}+{y}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\frac{{k}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}}\neq\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{1}}\Rightarrow{k}=\mathrm{6}\:{k}\neq\mathrm{15} \\ $$$${answer}\:{k}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$
Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 23/Jan/19
![Aliter kx+2y=5 (1) 6x+2y=2 (2) (k−6)x=3 [subtracting 2 from 1] x=(3/(k−6)) we want them to be parallel in other words they should intersect at ∞ ((k−6)/3)=(1/x)=0 [(1/∞)=0] ⇒k−6=0 ⇒k=6](Q53562.png)
$${Aliter} \\ $$$${kx}+\mathrm{2}{y}=\mathrm{5}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{2}{y}=\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\left({k}−\mathrm{6}\right){x}=\mathrm{3}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left[{subtracting}\:\mathrm{2}\:{from}\:\mathrm{1}\right] \\ $$$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{k}−\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$${we}\:{want}\:{them}\:{to}\:{be}\:{parallel}\:{in}\:{other}\:{words} \\ $$$${they}\:{should}\:{intersect}\:{at}\:\infty \\ $$$$\frac{{k}−\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}=\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\infty}=\mathrm{0}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{k}−\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{k}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$
