
Question Number 54541 by Tip Top last updated on 05/Feb/19

$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{of}\:{x}\:\mathrm{between}\:\:\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\:\:\mathrm{2}\pi\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{satisfy}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{equation}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{8}\:\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\:\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{AP}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{common}\:\mathrm{difference}. \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 05/Feb/19
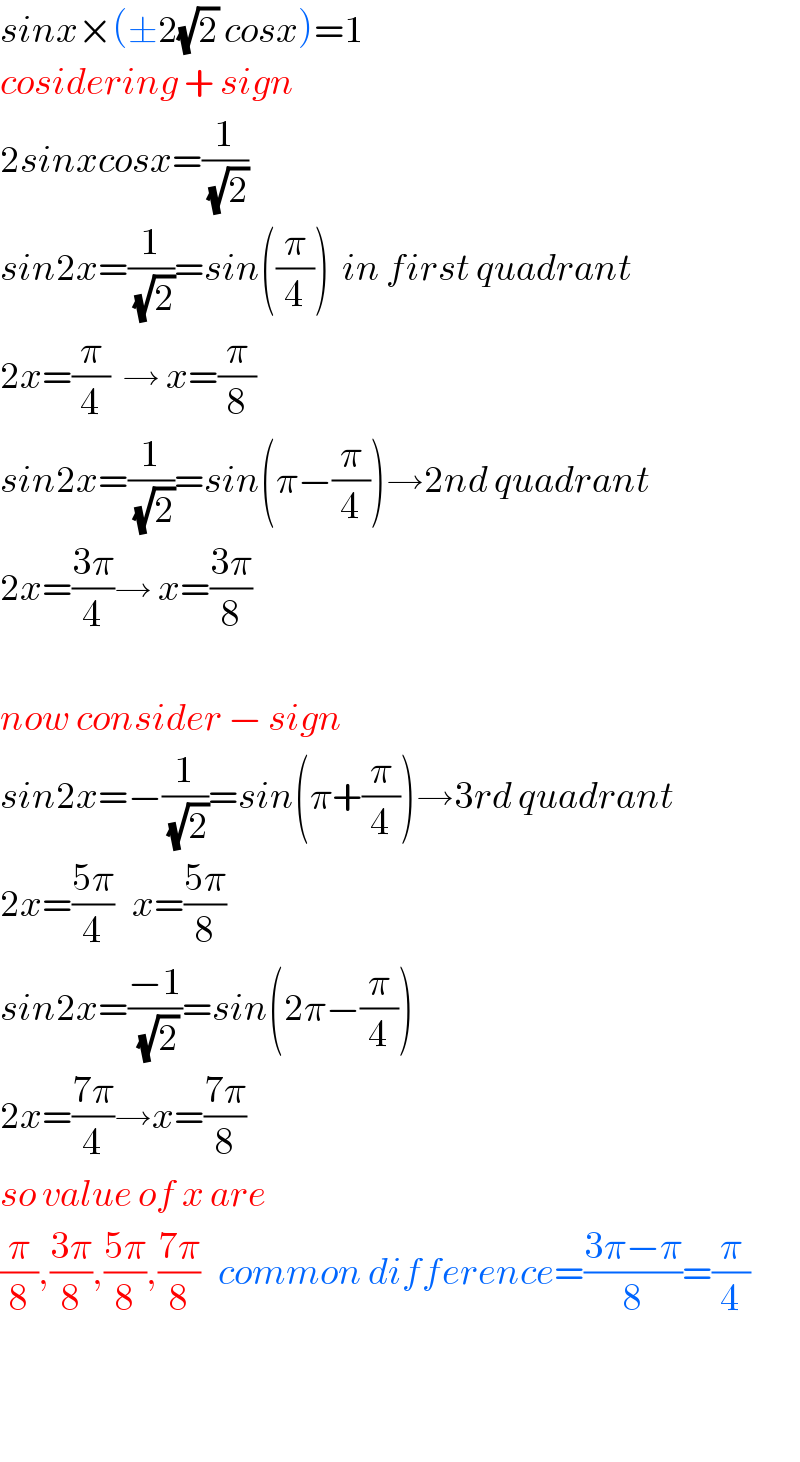
$${sinx}×\left(\pm\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:{cosx}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${cosidering}\:+\:{sign} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{sinxcosx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$${sin}\mathrm{2}{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}={sin}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\:\:{in}\:{first}\:{quadrant} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\:\:\rightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$${sin}\mathrm{2}{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}={sin}\left(\pi−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{2}{nd}\:{quadrant} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\rightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${now}\:{consider}\:−\:{sign} \\ $$$${sin}\mathrm{2}{x}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}={sin}\left(\pi+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{3}{rd}\:{quadrant} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}=\frac{\mathrm{5}\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\:\:\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{5}\pi}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$${sin}\mathrm{2}{x}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}={sin}\left(\mathrm{2}\pi−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}=\frac{\mathrm{7}\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\rightarrow{x}=\frac{\mathrm{7}\pi}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$${so}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x}\:{are} \\ $$$$\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}},\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{8}},\frac{\mathrm{5}\pi}{\mathrm{8}},\frac{\mathrm{7}\pi}{\mathrm{8}}\:\:\:{common}\:{difference}=\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi−\pi}{\mathrm{8}}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
