
Question Number 71235 by Rio Michael last updated on 13/Oct/19
![sinh[ln (x + (√(1 + x^2 ))) ] ≡ A. 2x B. (1/x) C. x^2 D. x](Q71235.png)
$${sinh}\left[{ln}\:\left({x}\:+\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}\:+\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\:\right]\:\equiv\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${A}.\:\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$${B}.\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}} \\ $$$${C}.\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${D}.\:\:{x} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 13/Oct/19
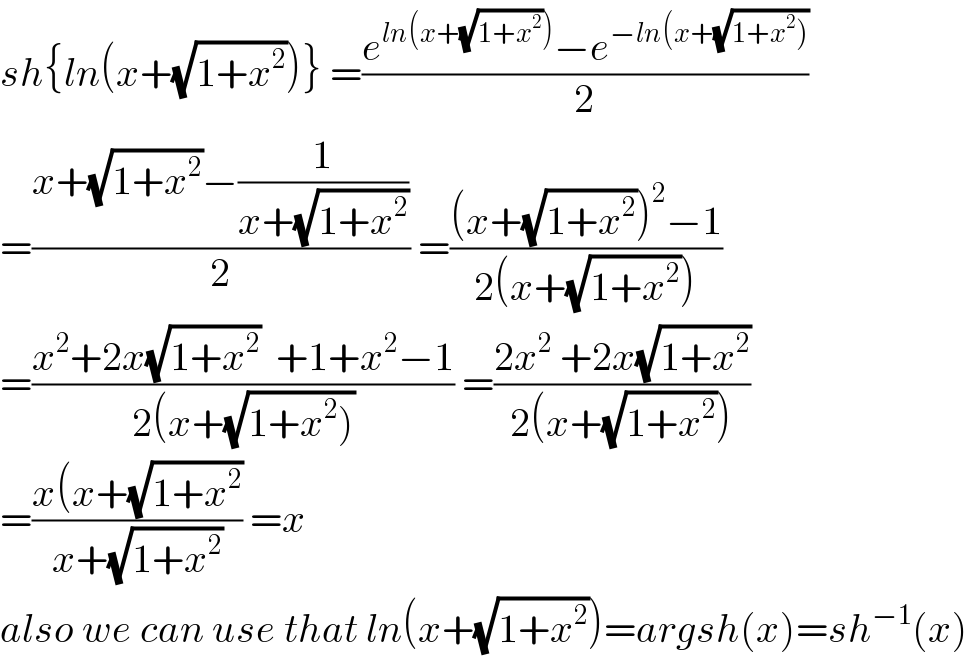
$${sh}\left\{{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\right\}\:=\frac{{e}^{{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)} −{e}^{−{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\right.} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\frac{\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:+\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left({x}+\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\right.}\:=\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2}{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{2}\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right.}{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:={x} \\ $$$${also}\:{we}\:{can}\:{use}\:{that}\:{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)={argsh}\left({x}\right)={sh}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right) \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 13/Oct/19

$$\mathrm{sinh}\:\alpha\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\alpha} −\mathrm{e}^{−\alpha} \right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{D}.\:{x} \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 13/Oct/19

$${i}\:{don}'{t}\:{understand}\:{the}\:{working}\:{sir} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 13/Oct/19

$$\mathrm{first},\:\mathrm{sorry}\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{made}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{typo}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{formula} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{sinh}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}\right)= \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\frac{\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}{{x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}={x} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 13/Oct/19

$${thanks}\:{sir} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 13/Oct/19
![let t=ln (x+(√(1+x^2 ))) e^t =x+(√(1+x^2 )) ...(i) e^(−t) =(1/(x+(√(1+x^2 ))))=−x+(√(1+x^2 )) −e^(−t) =x−(√(1+x^2 )) ...(ii) e^t −e^(−t) =2x ((e^t −e^(−t) )/2)=x ⇒sinh t=x i.e. sinh [ln (x+(√(1+x^2 )))]=x ⇒answer D](Q71263.png)
$${let}\:{t}=\mathrm{ln}\:\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$$${e}^{{t}} ={x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:...\left({i}\right) \\ $$$${e}^{−{t}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}=−{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$−{e}^{−{t}} ={x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:...\left({ii}\right) \\ $$$${e}^{{t}} −{e}^{−{t}} =\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$$\frac{{e}^{{t}} −{e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{2}}={x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{sinh}\:{t}={x} \\ $$$${i}.{e}.\:\mathrm{sinh}\:\left[\mathrm{ln}\:\left({x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\right]={x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{answer}\:{D} \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 13/Oct/19

$${thanks}\:{sirs} \\ $$
