
Question Number 80983 by jagoll last updated on 08/Feb/20

$${if}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{ae}^{{x}} −{b}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{ce}^{−{x}} }{{x}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${what}\:{is}\:{a}+{b}+{c}\:? \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 09/Feb/20
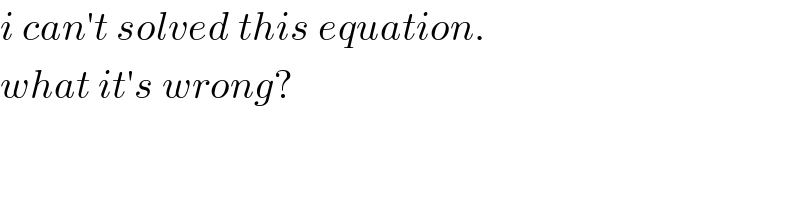
$${i}\:{can}'{t}\:{solved}\:{this}\:{equation}.\: \\ $$$${what}\:{it}'{s}\:{wrong}? \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 09/Feb/20

$${step}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{limit}\:{must}\:{be}\:\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}\:+{c}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{c}\:=\:−{a} \\ $$$${step}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{ae}^{{x}} −{b}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:−{ae}^{−{x}} }{{x}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}\:=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${L}\hat {\:}{hopital}\:{rule} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{ae}^{{x}} −{b}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+{ae}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{x}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${since}\:{denumerator}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:,\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{a}\:−{b}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{b}\:=\:\mathrm{2}{a} \\ $$$${L}\hat {\:}{hopital}\:{again} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{ae}^{{x}} +{b}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}−{ae}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2cos}\:{x}−{x}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow? \\ $$
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 09/Feb/20

$$\Rightarrow{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\frac{{ae}^{{x}} −{bsinx}\:+{c}\:{e}^{−{x}} }{{xsinx}}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\:\frac{{a}\:{e}^{{x}} −{bsinx}+{ce}^{−{x}} −\mathrm{2}{xsinx}}{{xsinx}}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {u}\left({x}\right)=={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {u}^{'} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:{and} \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {v}\left({x}\right)={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:{v}^{'} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:{with} \\ $$$${u}\left({x}\right)={ae}^{{x}} −{bsinx}\:+{ce}^{−{x}} −\mathrm{2}{xsinx}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${u}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{a}\:+{c}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{c}=−{a} \\ $$$${u}^{'} \left({x}\right)={ae}^{{x}} −{bcosx}−{ce}^{−{x}} −\mathrm{2}{sinx}−\mathrm{2}{x}\:{cosx} \\ $$$${u}^{'} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{a}−{b}−{c}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{a}−{b}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{b}=\mathrm{2}{a} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}+{b}+{c}\:=\mathrm{2}\left({b}+{c}\right)=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}−{a}\right)=\mathrm{2}{a} \\ $$$${if}\:{we}\:{get}\:{a}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{a}+{b}+{c}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 09/Feb/20

$${you}\:{are}\:{right}\:{sir} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 09/Feb/20

$${how}\:{to}\:{get}\:{a}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\:? \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 09/Feb/20
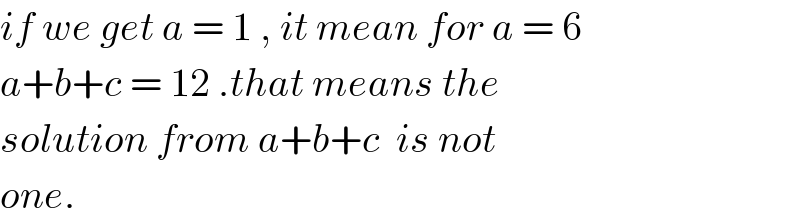
$${if}\:{we}\:{get}\:{a}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\:,\:{it}\:{mean}\:{for}\:{a}\:=\:\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${a}+{b}+{c}\:=\:\mathrm{12}\:.{that}\:{means}\:{the} \\ $$$${solution}\:{from}\:{a}+{b}+{c}\:\:{is}\:{not}\: \\ $$$${one}. \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 09/Feb/20

$${have}\:{you}\:{checked}\:{sir}? \\ $$$${i}\:{don}'{t}\:{think}\:{the}\:{answer}\:{is}\:{correct}. \\ $$$${example}:\:{a}=\mathrm{1},{b}=\mathrm{2},{c}=−\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}} −\mathrm{2sin}\:{x}−{e}^{−{x}} }{{x}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}} −\mathrm{2cos}\:{x}+{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} +\mathrm{2sin}\:{x}−{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}−{x}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{0}\neq\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${my}\:{answer}\:{is}: \\ $$$${there}\:{exist}\:{no}\:{values}\:{for}\:{a},{b},\:{c}\:{such} \\ $$$${that}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{ae}^{{x}} −{b}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{ce}^{−{x}} }{{x}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}=\mathrm{2}. \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 09/Feb/20

$${yes}\:{sir}.\:{i}\:{think}\:{it}\:{question}\:{not}\:{right} \\ $$
