
Question Number 83352 by jagoll last updated on 01/Mar/20
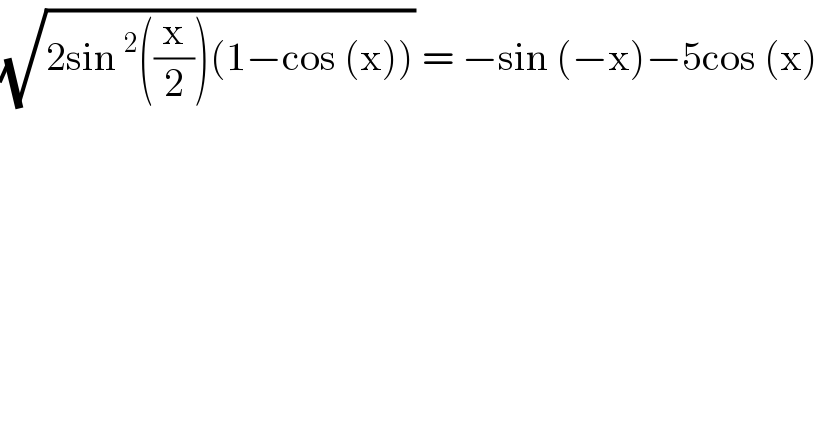
$$\sqrt{\mathrm{2sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\right)}\:=\:−\mathrm{sin}\:\left(−\mathrm{x}\right)−\mathrm{5cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 01/Mar/20
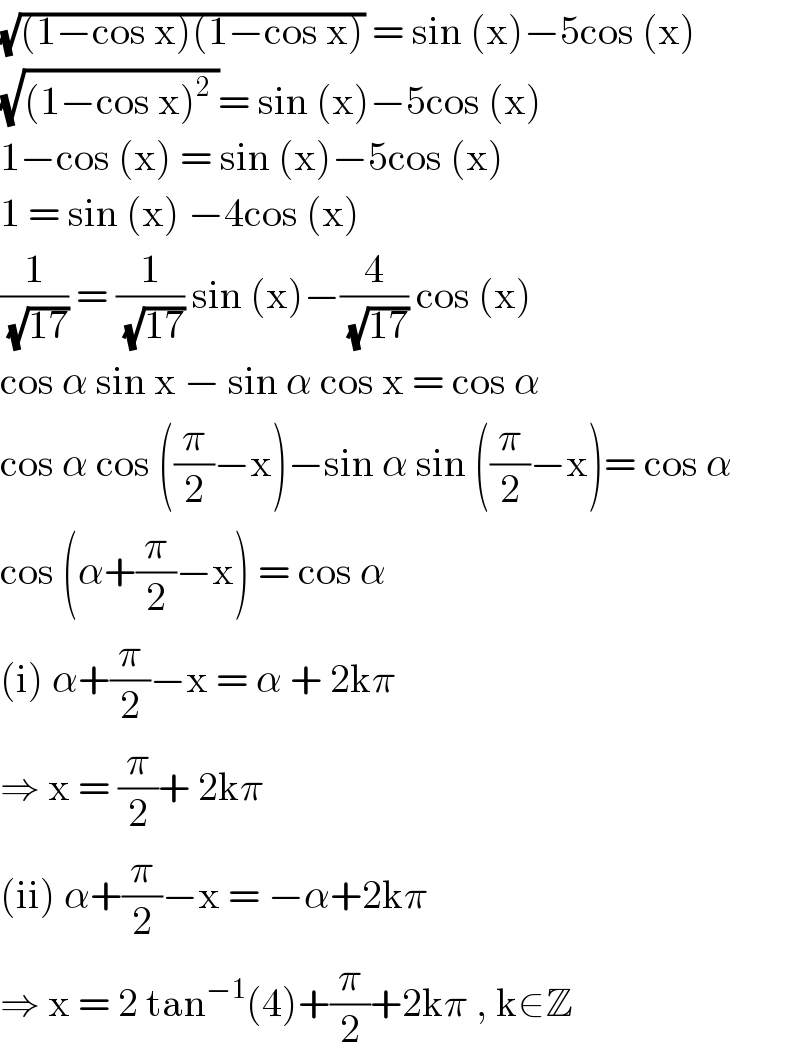
$$\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\right)}\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)−\mathrm{5cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:}=\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)−\mathrm{5cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)−\mathrm{5cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:−\mathrm{4cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}\:−\:\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha\:\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{x}\right)−\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{x}\right)=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\alpha+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{i}\right)\:\alpha+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{x}\:=\:\alpha\:+\:\mathrm{2k}\pi \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+\:\mathrm{2k}\pi \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{ii}\right)\:\alpha+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{x}\:=\:−\alpha+\mathrm{2k}\pi \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{4}\right)+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2k}\pi\:,\:\mathrm{k}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 01/Mar/20

$$\mathrm{how}\:\mathrm{do}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{get}\:\mathrm{2arctan}\:\mathrm{4}\:? \\ $$$$\alpha+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−{x}=−\alpha+\mathrm{2}{k}\pi \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}=\mathrm{2}\alpha+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2}{k}\pi \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 01/Mar/20
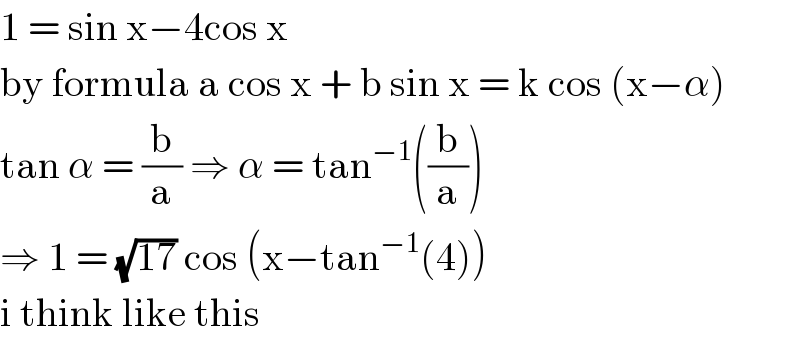
$$\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{4cos}\:\mathrm{x}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{formula}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}\:+\:\mathrm{b}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:\mathrm{k}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}−\alpha\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{tan}\:\alpha\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}\:\Rightarrow\:\alpha\:=\:\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{1}\:=\:\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{4}\right)\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{think}\:\mathrm{like}\:\mathrm{this} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 02/Mar/20
![⇒(√((1−cosx)(1−cosx)))=sinx −5cosx ⇒ ∣1−cosx∣=sinx−5cosx case1 1−cosx =sinx−5cosx ⇒1−cosx−sinx +5cosx=0⇒ 4cosx−sinx =−1 ⇒(√(17)){(4/(√(17))) cosx −(1/(√(17)))sinx}=−1 ⇒ cosα cosx−sinα sinx =−(1/(√(17))) ( cosα=(4/(√(17))) and sinα=(1/(√(17)))⇒ tanα =(1/4) ⇒α=arctan((1/4))=(π/2) −arctan(4) ⇒ cos(α−x)=−(1/(√(17))) =cos(α_0 )⇒α−x=α_0 [2π] or α−x=−α_0 [2π ⇒x=α−α_0 [2π] or x=α +α_0 [2π] with α_0 =arcos((1/(√(17)))). case2 1−cosx=−sinx +5cosx ⇒1−cosx+sinx −5cosx =0 ⇒ 1−6cosx +sinx =0 ⇒−6cosx +sinx =−1 ⇒6cosx−sinx=1 ⇒ (√(37)){(6/(√(37))) cosx −(1/(√(37)))sinx}=1 ⇒ cosαcosx−sinα sinx =(1/(√(37))) with α =artan((1/6))=(π/2)−arctan(6) we follow the same way....](Q83424.png)
$$\Rightarrow\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}−{cosx}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}−{cosx}\right)}={sinx}\:−\mathrm{5}{cosx}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mid\mathrm{1}−{cosx}\mid={sinx}−\mathrm{5}{cosx} \\ $$$${case}\mathrm{1}\:\:\mathrm{1}−{cosx}\:={sinx}−\mathrm{5}{cosx}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}−{cosx}−{sinx}\:+\mathrm{5}{cosx}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}{cosx}−{sinx}\:=−\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}\left\{\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\:{cosx}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}{sinx}\right\}=−\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${cos}\alpha\:{cosx}−{sin}\alpha\:{sinx}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\:\:\left(\:\:{cos}\alpha=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\:{and}\:{sin}\alpha=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\Rightarrow\right. \\ $$$${tan}\alpha\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow\alpha={arctan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:−{arctan}\left(\mathrm{4}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${cos}\left(\alpha−{x}\right)=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\:={cos}\left(\alpha_{\mathrm{0}} \right)\Rightarrow\alpha−{x}=\alpha_{\mathrm{0}} \left[\mathrm{2}\pi\right]\:{or}\:\alpha−{x}=−\alpha_{\mathrm{0}} \left[\mathrm{2}\pi\right. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\alpha−\alpha_{\mathrm{0}} \left[\mathrm{2}\pi\right]\:{or}\:\:{x}=\alpha\:+\alpha_{\mathrm{0}} \left[\mathrm{2}\pi\right]\:\:{with}\:\alpha_{\mathrm{0}} ={arcos}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}}\right). \\ $$$${case}\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{1}−{cosx}=−{sinx}\:+\mathrm{5}{cosx}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}−{cosx}+{sinx}\:−\mathrm{5}{cosx}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{6}{cosx}\:+{sinx}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow−\mathrm{6}{cosx}\:+{sinx}\:=−\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{6}{cosx}−{sinx}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{37}}\left\{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{37}}}\:{cosx}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{37}}}{sinx}\right\}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${cos}\alpha{cosx}−{sin}\alpha\:{sinx}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{37}}}\:\:\:{with}\:\alpha\:={artan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\right)=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−{arctan}\left(\mathrm{6}\right) \\ $$$${we}\:{follow}\:{the}\:{same}\:{way}.... \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 02/Mar/20
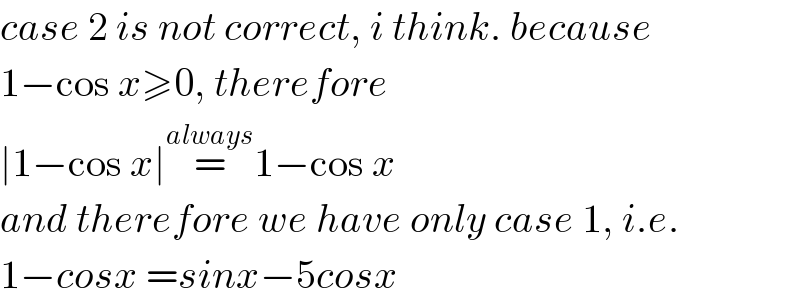
$${case}\:\mathrm{2}\:{is}\:{not}\:{correct},\:{i}\:{think}.\:{because} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\geqslant\mathrm{0},\:{therefore} \\ $$$$\mid\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\mid\overset{{always}} {=}\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$${and}\:{therefore}\:{we}\:{have}\:{only}\:{case}\:\mathrm{1},\:{i}.{e}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}−{cosx}\:={sinx}−\mathrm{5}{cosx} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 02/Mar/20
$${you}\:{are}\:{right}\:{thank}\:{you}... \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 01/Mar/20
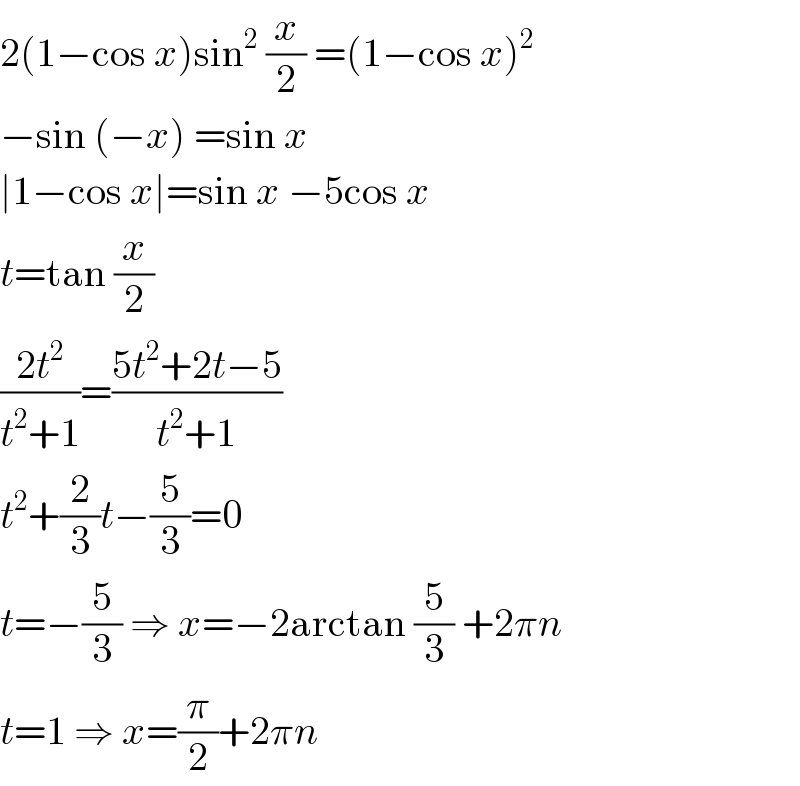
$$\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right)\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{sin}\:\left(−{x}\right)\:=\mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$\mid\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\mid=\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:−\mathrm{5cos}\:{x} \\ $$$${t}=\mathrm{tan}\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{5}{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{t}−\mathrm{5}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}{t}−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{3}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${t}=−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}=−\mathrm{2arctan}\:\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{3}}\:+\mathrm{2}\pi{n} \\ $$$${t}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2}\pi{n} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 01/Mar/20
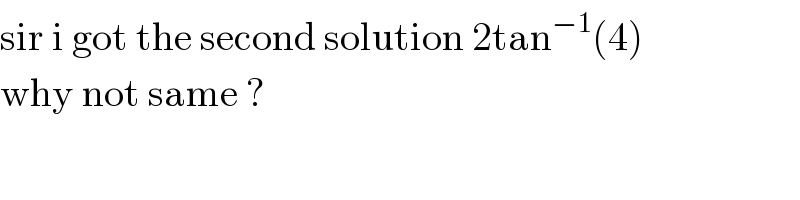
$$\mathrm{sir}\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{got}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{second}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{2tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{why}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{same}\:? \\ $$
