
Question Number 84109 by Power last updated on 09/Mar/20
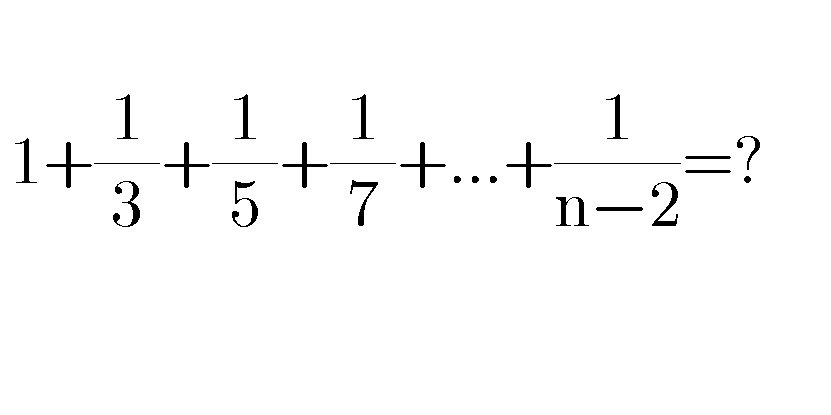
Commented by mahdi last updated on 09/Mar/20
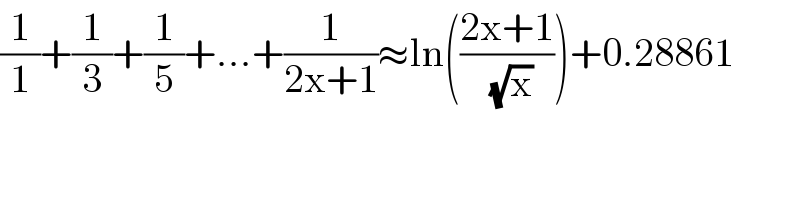
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}+...+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}}\approx\mathrm{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}}\right)+\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{28861} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 09/Mar/20
![A_n =1+(1/3) +(1/5) +....+(1/(n−2)) case 1 n=2p+1 ⇒ A_n =1+(1/3) +(1/5)+....+(1/(2p−1)) =1+(1/2) +(1/3)+(1/4) +.....+(1/(2p−1)) +(1/(2p)) −(1/2)−(1/4)−...−(1/(2p)) =H_(2p) −(1/2) H_p we have p=[((n−1)/2)] ⇒ A_n =H_(2[((n−1)/2)]) −(1/2)H_([((n−1)/2)]) case 2 n=2p ⇒ A_n =1+(1/3) +(1/5) +....+(1/(2(p−1))) =1+(1/2)+(1/3)+(1/4)+....+(1/(2p−4))+(1/(2p−3))+(1/(2(p−1))) −(1/2)−(1/4)−....−(1/(2(p−2))) =H_(2p−2) −(1/2)H_(p−2) =H_(2[(n/2)]−2) −(1/2)H_([(n/2)]−2) H_N =Σ_(k=1) ^N (1/k)](Q84147.png)
$${A}_{{n}} =\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\:+....+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{1}\:\:{n}=\mathrm{2}{p}+\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\:{A}_{{n}} =\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}+....+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{p}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:+.....+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{p}−\mathrm{1}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{p}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−...−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{p}} \\ $$$$={H}_{\mathrm{2}{p}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:{H}_{{p}} \:\:\:\:{we}\:{have}\:{p}=\left[\frac{{n}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} ={H}_{\mathrm{2}\left[\frac{{n}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{H}_{\left[\frac{{n}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]} \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{2}\:\:{n}=\mathrm{2}{p}\:\Rightarrow\:{A}_{{n}} =\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\:+....+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left({p}−\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}+....+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{p}−\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{p}−\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left({p}−\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−....−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left({p}−\mathrm{2}\right)}\:={H}_{\mathrm{2}{p}−\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{H}_{{p}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$={H}_{\mathrm{2}\left[\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]−\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{H}_{\left[\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${H}_{{N}} =\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{N}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}} \\ $$
Answered by mind is power last updated on 09/Mar/20
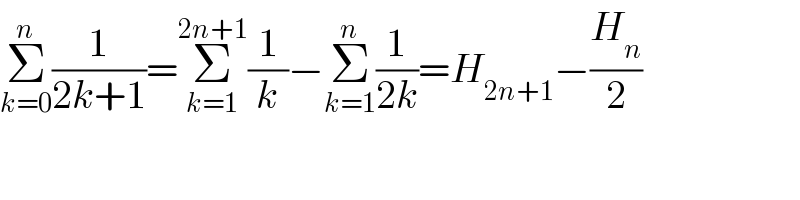
$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1}}=\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}}−\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}}={H}_{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} −\frac{{H}_{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
