
Question Number 97108 by M±th+et+s last updated on 06/Jun/20
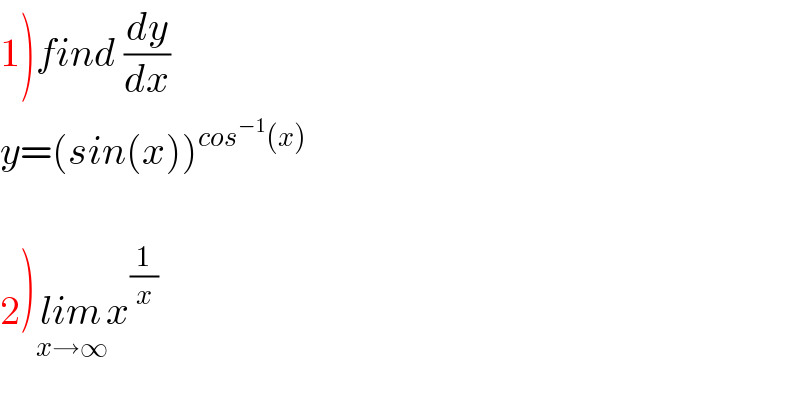
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right){find}\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}} \\ $$$${y}=\left({sin}\left({x}\right)\right)^{{cos}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}x}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}} \\ $$
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 06/Jun/20
$${thanks}\:{for}\:{solutions} \\ $$
Answered by Sourav mridha last updated on 06/Jun/20
![1)(dy/dx)=(d/dx)e^(cos^(−1) (x).lnsin(x)) =(sin(x))^(cos^(−1) (x)) [cotx.cos^(−1) (x)−((ln(sin(x)))/(√(1−x^2 )))]](Q97111.png)
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\frac{\boldsymbol{{dy}}}{\boldsymbol{{dx}}}=\frac{\boldsymbol{{d}}}{\boldsymbol{{dx}}}\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\mathrm{cos}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right).\boldsymbol{{lnsin}}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)} \: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\left(\boldsymbol{{sin}}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)\right)^{\mathrm{cos}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)} \left[\boldsymbol{{cotx}}.\mathrm{cos}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)−\frac{\boldsymbol{{ln}}\left(\boldsymbol{{sin}}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)\right)}{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\right] \\ $$
Answered by Sourav mridha last updated on 06/Jun/20
![2)u=x^(1/x) ⇒ ⇒ln(u)=((ln(x))/x) ⇒lim_(x→∞) [ln(u)]=lim_(x→∞) [((ln(x))/x)]{(∞/∞) form using LHopital} =0 ⇒lim_(x→∞) [(u)]=e^0 =1](Q97113.png)
$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\boldsymbol{{u}}=\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}}} \Rightarrow \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\boldsymbol{{ln}}\left(\boldsymbol{{u}}\right)=\frac{\boldsymbol{{ln}}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)}{\boldsymbol{{x}}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\mathrm{l}\boldsymbol{{n}}\left(\boldsymbol{{u}}\right)\right]=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\frac{\boldsymbol{{ln}}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)}{\boldsymbol{{x}}}\right]\left\{\frac{\infty}{\infty}\:\boldsymbol{{form}}\:\boldsymbol{{using}}\:\boldsymbol{{LHopital}}\right\} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\left(\boldsymbol{{u}}\right)\right]=\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by abdomathmax last updated on 06/Jun/20
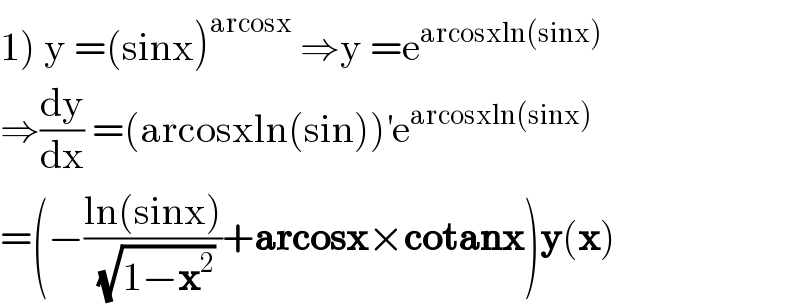
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{y}\:=\left(\mathrm{sinx}\right)^{\mathrm{arcosx}} \:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{arcosxln}\left(\mathrm{sinx}\right)} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\:=\left(\mathrm{arcosxln}\left(\mathrm{sin}\right)\right)^{'} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{arcosxln}\left(\mathrm{sinx}\right)} \\ $$$$=\left(−\frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{sinx}\right)}{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }}+\boldsymbol{\mathrm{arcosx}}×\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cotanx}}\right)\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}\right) \\ $$
Answered by abdomathmax last updated on 06/Jun/20
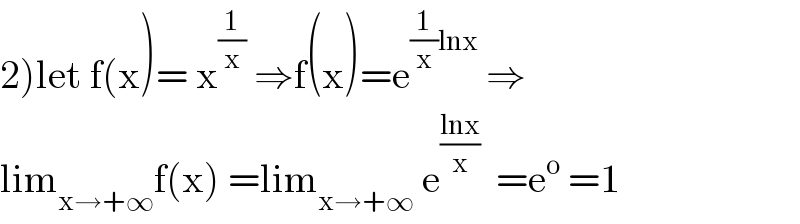
$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\:\mathrm{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}} \:\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{lnx}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow+\infty} \mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\mathrm{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{lnx}}{\mathrm{x}}} \:\:=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{o}} \:=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
