
Question Number 98119 by bobhans last updated on 11/Jun/20
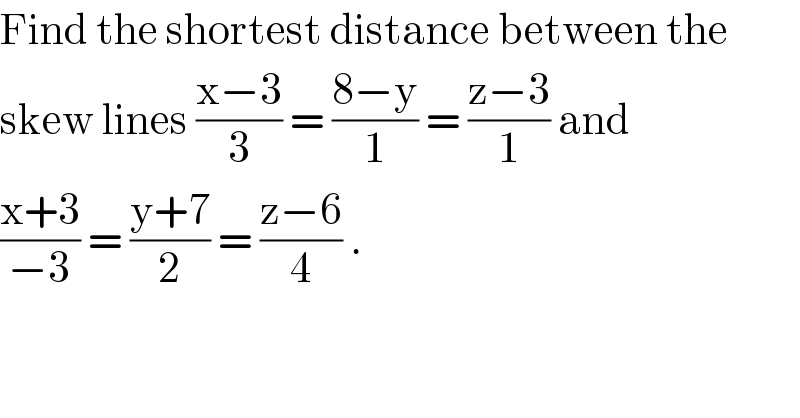
$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{shortest}\:\mathrm{distance}\:\mathrm{between}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{skew}\:\mathrm{lines}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{3}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{1}}\:\mathrm{and}\: \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}}{−\mathrm{3}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{4}}\:. \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 11/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{shortest}\:\mathrm{distance}\:\mathrm{lies}\:\mathrm{along}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{direction} \\ $$$$\mathrm{which}\:\bot\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{both}\:\mathrm{lines}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{given} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{cross}\:\mathrm{product}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{vectors}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{long} \\ $$$$\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{two}\:\mathrm{lines},\:{l}_{\mathrm{1}} ,{l}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\overset{\rightarrow} {\mathrm{n}}\:=\:\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{3}\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{1}}\\{−\mathrm{3}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}}\end{vmatrix} \\ $$$$\overset{\rightarrow} {\mathrm{n}}\:=\:−\mathrm{6}\hat {{i}}−\mathrm{15}\hat {\mathrm{j}}\:+\mathrm{3}\hat {\mathrm{k}}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{shortest}\:\mathrm{distance}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{SD}\:=\:\mathrm{A}\overset{\rightarrow} {\mathrm{B}}\:.\:\overset{\rightarrow} {\mathrm{n}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{30}}\:}\:\left(\mathrm{12}+\mathrm{75}+\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{90}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{30}}}\:=\:\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{30}}\: \\ $$
