Question Number 27847 by NECx last updated on 15/Jan/18
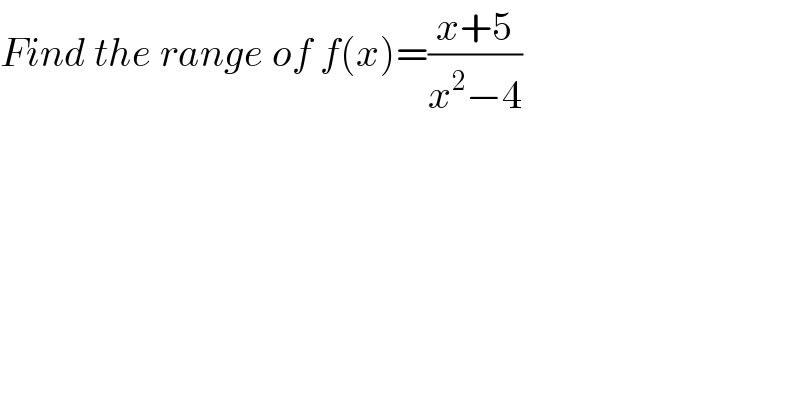
$${Find}\:{the}\:{range}\:{of}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{x}+\mathrm{5}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Commented by NECx last updated on 16/Jan/18

$${please}\:{help} \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 17/Jan/18
![y=((x+5)/(x^2 −4)) x^2 y−x−(4y+5)=0 x∈R⇒Δ≥0 (−1)^2 −4(y)(−)(4y+5)≥0 1+16y^2 +20y≥0 16y^2 +20y+1≥0 (y−(−(5/8)+((√(21))/8)))(y−(−(5/8)−((√(21))/8)))≥0 ∵ A quadratic expression has sine same as coefficient of x^2 except in between roots. y∈(−∞,−(5/8)−((√(21))/8)]∪[−(5/8)+((√(21))/8),∞)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q27891.png)
$${y}=\frac{{x}+\mathrm{5}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}−{x}−\left(\mathrm{4}{y}+\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}\in\mathrm{R}\Rightarrow\Delta\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\left({y}\right)\left(−\right)\left(\mathrm{4}{y}+\mathrm{5}\right)\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{16}{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{20}{y}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{16}{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{20}{y}+\mathrm{1}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({y}−\left(−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{8}}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{21}}}{\mathrm{8}}\right)\right)\left({y}−\left(−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{21}}}{\mathrm{8}}\right)\right)\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\because\:\mathrm{A}\:\mathrm{quadratic}\:\mathrm{expression}\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{sine} \\ $$$$\mathrm{same}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{coefficient}\:\mathrm{of}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{except}\:\mathrm{in} \\ $$$$\mathrm{between}\:\mathrm{roots}. \\ $$$${y}\in\left(−\infty,−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{21}}}{\mathrm{8}}\right]\cup\left[−\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{8}}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{21}}}{\mathrm{8}},\infty\right) \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 16/Jan/18
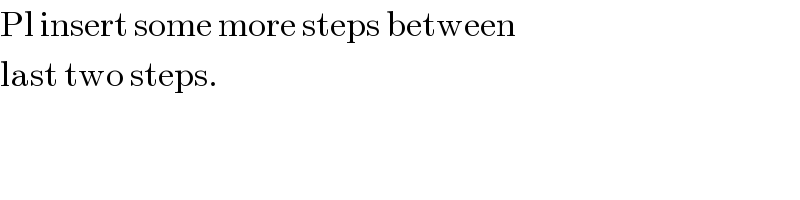
$$\mathrm{Pl}\:\mathrm{insert}\:\mathrm{some}\:\mathrm{more}\:\mathrm{steps}\:\mathrm{between} \\ $$$$\mathrm{last}\:\mathrm{two}\:\mathrm{steps}. \\ $$
