Question Number 101373 by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 02/Jul/20
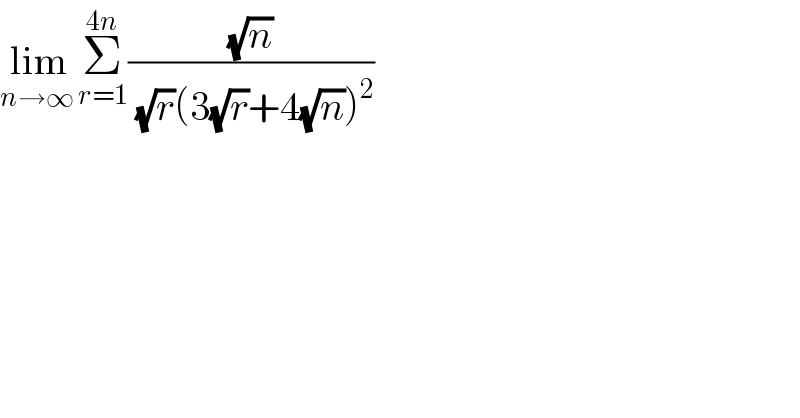
$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty\:} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{{r}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{4}{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\sqrt{{n}}}{\:\sqrt{{r}}\left(\mathrm{3}\sqrt{{r}}+\mathrm{4}\sqrt{{n}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 02/Jul/20
![(1/n)lim_(n→∞) Σ_(r=1) ^(4n) ((n/r))^(3/2) .(1/((3+4(√(n/r)))^2 ))=∫_0 ^4 (1/x^(3/2) ).(1/((3+(4/x^(1/2) ))^2 ))dx=∫_0 ^4 ((1/x^(3/2) )/((3+(4/x^(1/2) ))^2 ))dx −(1/2)∫_0 ^4 (((−2)/x^(3/2) )/((3+(4/x^(1/2) ))^2 ))dx=−(1/2)∫_∞ ^5 (dt/t^2 )=(1/2)[(1/t)]_∞ ^5 =(1/(10)) Is it right???????](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q101391.png)
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{{r}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{4}{n}} {\sum}}\left(\frac{{n}}{{r}}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} .\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\frac{{n}}{{r}}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }.\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }}{\left(\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \frac{\frac{−\mathrm{2}}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }}{\left(\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\infty} ^{\mathrm{5}} \frac{{dt}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}\right]_{\infty} ^{\mathrm{5}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Is}\:{it}\:{right}??????? \\ $$
