Question Number 120839 by bramlexs22 last updated on 03/Nov/20
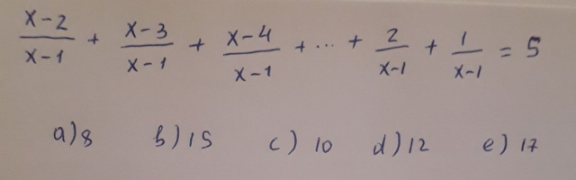
Answered by mindispower last updated on 03/Nov/20
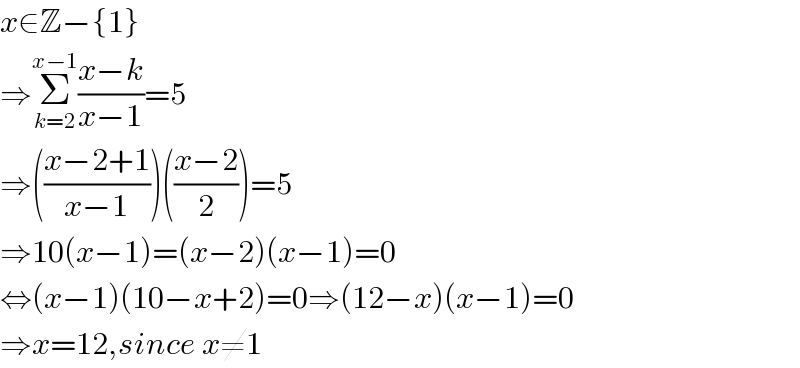
$${x}\in\mathbb{Z}−\left\{\mathrm{1}\right\} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\underset{{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}\frac{{x}−{k}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{10}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{10}−{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{12}−{x}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{12},{since}\:{x}\neq\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by bramlexs22 last updated on 03/Nov/20

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$
Answered by talminator2856791 last updated on 03/Nov/20
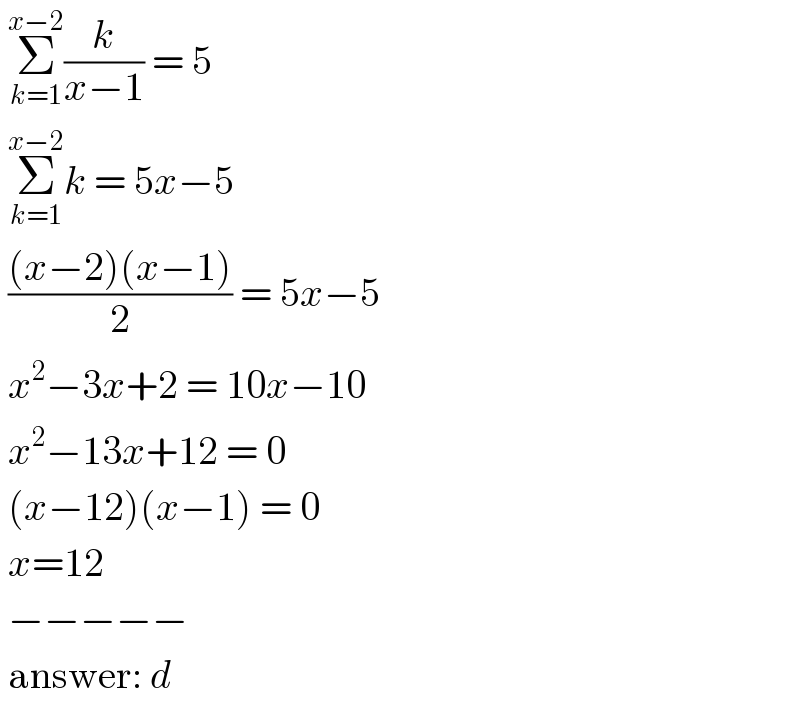
$$\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{x}−\mathrm{2}} {\sum}}\frac{{k}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{x}−\mathrm{2}} {\sum}}{k}\:=\:\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\:\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\:\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{10}{x}−\mathrm{10} \\ $$$$\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13}{x}+\mathrm{12}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\left({x}−\mathrm{12}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:{x}=\mathrm{12} \\ $$$$\:−−−−− \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{answer}:\:{d} \\ $$
Answered by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 03/Nov/20
![a=x−2 d=−1 T_n =a+(n−1)d 1=(x−2)+(n−1)×−1 1=(x−2)−n+1 n=x−2 LHS (((x−2)+(x−3)+(x−4)+...+1)/(x−1)) ((x−2)/2)[x−2+1]×(1/(x−1)) →(n/2)(a+l) =((x−2)/2) ((x−2)/2)=5 x=12](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q120860.png)
$${a}={x}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${d}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${T}_{{n}} ={a}+\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){d} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}=\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)+\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)×−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}=\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)−{n}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${n}={x}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${LHS} \\ $$$$\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)+\left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right)+\left({x}−\mathrm{4}\right)+…+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\frac{{x}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[{x}−\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}\right]×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:\rightarrow\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({a}+{l}\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\frac{{x}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{12} \\ $$
