Question Number 91371 by jagoll last updated on 30/Apr/20
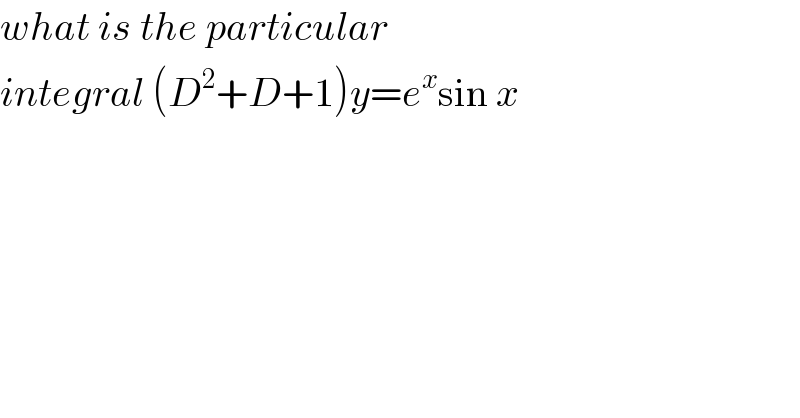
$${what}\:{is}\:{the}\:{particular}\: \\ $$$${integral}\:\left({D}^{\mathrm{2}} +{D}+\mathrm{1}\right){y}={e}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 30/Apr/20
![y_p = ((e^x sin x)/(D^2 +D+1)) y_p = ((xe^x sin x)/(2D+1)) = −[ (2D−1)xe^x sin x ] = −2[e^x sin x+xe^x sin x+xe^x cos x] +xe^x sin x = −2e^x sin x−2xe^x sin x−2xe^x cos x + xe^x cos x = −2e^x sin x−2xe^x sin x−xe^x cos x = e^x (−2sin x−2xsin x−xcos x)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q91391.png)
$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +{D}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:\frac{{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{\mathrm{2}{D}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\:−\left[\:\left(\mathrm{2}{D}−\mathrm{1}\right){xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\right] \\ $$$$=\:−\mathrm{2}\left[{e}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right] \\ $$$$+{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$=\:−\mathrm{2}{e}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$$+\:{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$$=\:−\mathrm{2}{e}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}\:{x}−{xe}^{{x}} \mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$$=\:{e}^{{x}} \:\left(−\mathrm{2sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}{x}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}−{x}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right) \\ $$
