Question Number 177578 by BaliramKumar last updated on 07/Oct/22
Commented by BaliramKumar last updated on 07/Oct/22
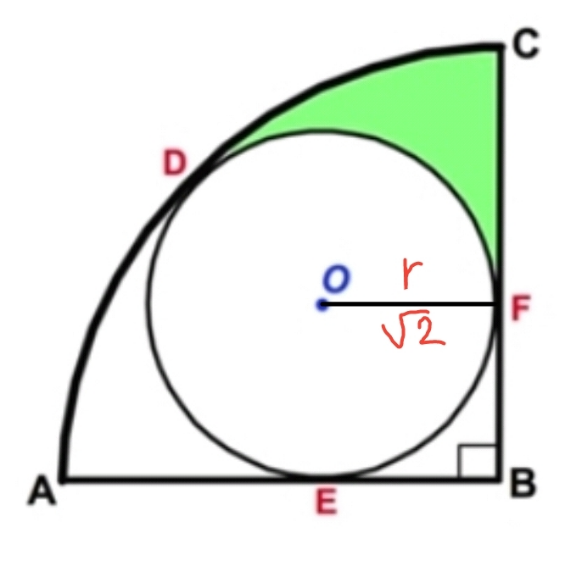
area of green colour
Commented by som(math1967) last updated on 07/Oct/22

$$\:\frac{\pi\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{1}\:? \\ $$
Commented by BaliramKumar last updated on 07/Oct/22

$${yes}\:{sir} \\ $$
Commented by som(math1967) last updated on 07/Oct/22
![Ar .of circle=2π let R=rad of quadrant OB=R−(√2) OABC square ∴OB=(√2)×(√2)=2 ∴R=2+(√2) ar. of quadrant=(1/4)π(2+(√2))^2 ar.of quadrant form with OABC (1/4)×π×((√2))^2 =(π/2) A_(green) =(1/2)[(1/4)π(2+(√2))^2 −2π−(2−(π/2))] =(1/2)[(1/4)π×2(3+(√2))−((3π)/2)−2] =(( π(√2))/2) −1 sq unit](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q177601.png)
$$\:{Ar}\:.{of}\:\:{circle}=\mathrm{2}\pi \\ $$$${let}\:{R}={rad}\:{of}\:{quadrant} \\ $$$${OB}={R}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${OABC}\:{square}\:\therefore{OB}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}×\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\therefore{R}=\mathrm{2}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:{ar}.\:{of}\:{quadrant}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\pi\left(\mathrm{2}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${ar}.{of}\:{quadrant}\:{form}\:{with}\:{OABC} \\ $$$$\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}×\pi×\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:{A}_{{green}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\pi\left(\mathrm{2}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\pi−\left(\mathrm{2}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\pi×\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{3}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{3}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\:\pi\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{1}\:{sq}\:{unit} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by som(math1967) last updated on 07/Oct/22

Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 07/Oct/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Answered by cherokeesay last updated on 07/Oct/22

Commented by BaliramKumar last updated on 07/Oct/22

$${great}\:{sir} \\ $$
