Question Number 136670 by rexford last updated on 24/Mar/21
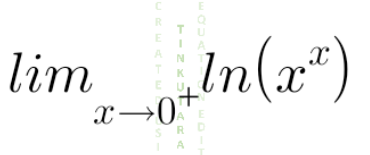
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 24/Mar/21

$$\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 24/Mar/21
![ln x^x =xln x ∀x>0 lim_(x→0^+ ) xln x =lim_(t→+∞) ((ln (1/t))/t) =−lim_(t→+∞) ((ln t)/t) = =−lim_(t→+∞) (((d/dt)[ln t])/((d/dt)[t])) =−lim_(t→+∞) ((1/t)/1) =0](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q136675.png)
$$\mathrm{ln}\:{x}^{{x}} \:={x}\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\:\forall{x}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:{x}\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\:=\underset{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}}{{t}}\:=−\underset{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:{t}}{{t}}\:= \\ $$$$=−\underset{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\left[\mathrm{ln}\:{t}\right]}{\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\left[{t}\right]}\:=−\underset{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}}{\mathrm{1}}\:=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by rexford last updated on 24/Mar/21

$${thanks}\:{very}\:{much}\:{for}\:{your}\:{time} \\ $$
