Question Number 134708 by bramlexs22 last updated on 06/Mar/21
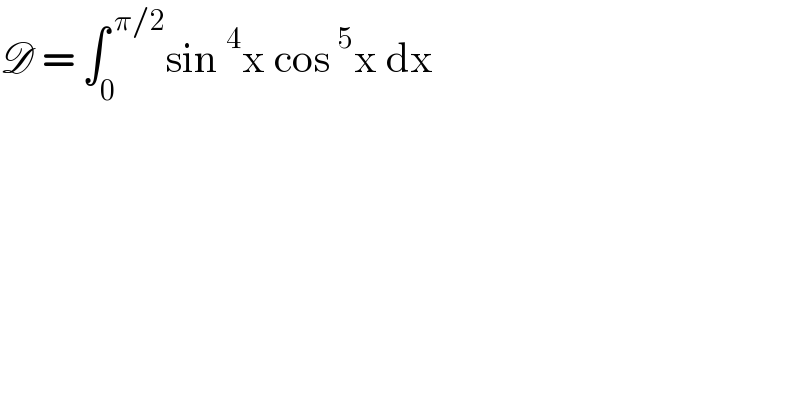
$$\mathscr{D}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\pi/\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{4}} \mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{5}} \mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{dx}\: \\ $$
Answered by john_santu last updated on 06/Mar/21
![D = ∫_0 ^( π/2) sin^4 x(1−sin^2 x)^2 cos x dx let u= sin x , determinant (((u=1(upper limit))),((u=0 (lower limit)))) D = ∫_0 ^( 1) u^4 (u^4 −2u^2 +1) du D = ∫_0 ^( 1) (u^8 −2u^6 +u^4 )du D = [(u^9 /9)−((2u^7 )/7) +(u^5 /5) ]_0 ^1 D = (1/9)−(2/7)+(1/5) = ((35−90+63)/(315)) D = (8/(315)) •](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q134709.png)
$$\mathscr{D}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\pi/\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{4}} {x}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$${let}\:{u}=\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:,\:\begin{array}{|c|c|}{{u}=\mathrm{1}\left({upper}\:{limit}\right)}\\{{u}=\mathrm{0}\:\left({lower}\:{limit}\right)}\\\hline\end{array} \\ $$$$\mathscr{D}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} {u}^{\mathrm{4}} \left({u}^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{2}{u}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\:{du}\: \\ $$$$\mathscr{D}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\mathrm{1}} \left({u}^{\mathrm{8}} −\mathrm{2}{u}^{\mathrm{6}} +{u}^{\mathrm{4}} \right){du} \\ $$$$\mathscr{D}\:=\:\left[\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{9}} }{\mathrm{9}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}{u}^{\mathrm{7}} }{\mathrm{7}}\:+\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}}\:\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathscr{D}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{7}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{35}−\mathrm{90}+\mathrm{63}}{\mathrm{315}} \\ $$$$\mathscr{D}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{315}}\:\bullet \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 06/Mar/21
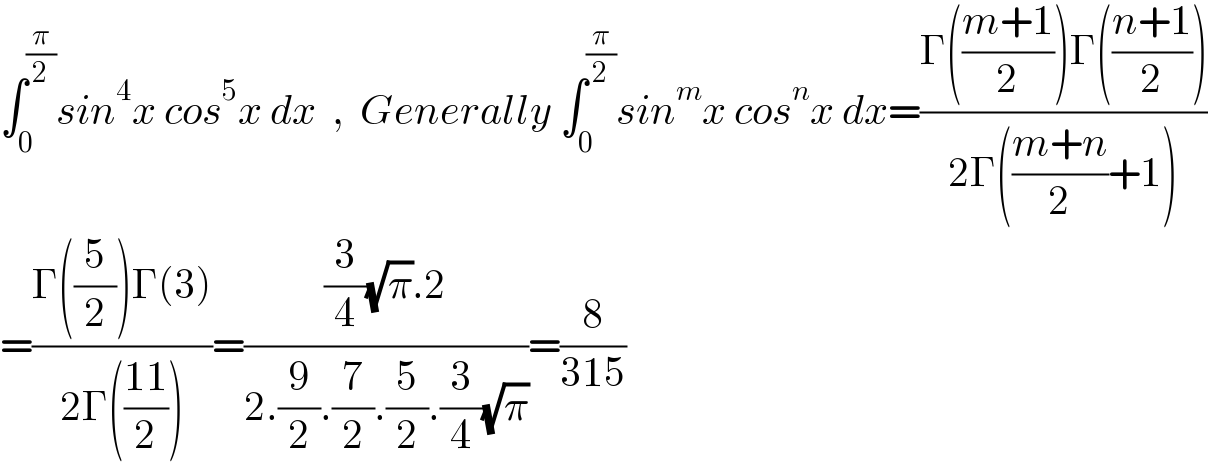
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {sin}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}\:{cos}^{\mathrm{5}} {x}\:{dx}\:\:,\:\:{Generally}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} {sin}^{{m}} {x}\:{cos}^{{n}} {x}\:{dx}=\frac{\Gamma\left(\frac{{m}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\Gamma\left(\frac{{n}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{2}\Gamma\left(\frac{{m}+{n}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$=\frac{\Gamma\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\Gamma\left(\mathrm{3}\right)}{\mathrm{2}\Gamma\left(\frac{\mathrm{11}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{4}}\sqrt{\pi}.\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}.\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{4}}\sqrt{\pi}}=\frac{\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{315}} \\ $$
