Question Number 257 by abcd last updated on 25/Jan/15
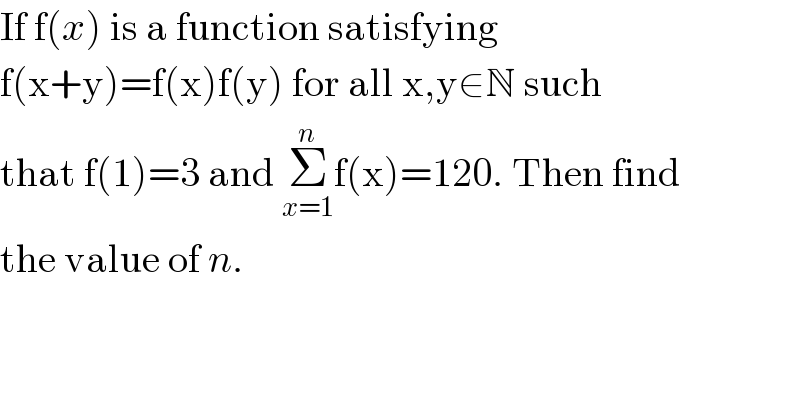
$$\mathrm{If}\:\mathrm{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{function}\:\mathrm{satisfying} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}\right)=\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{all}\:\mathrm{x},\mathrm{y}\in\mathbb{N}\:\mathrm{such} \\ $$$$\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{and}\:\underset{{x}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{120}.\:\mathrm{Then}\:\mathrm{find} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{of}\:{n}. \\ $$
Answered by 123456 last updated on 17/Dec/14
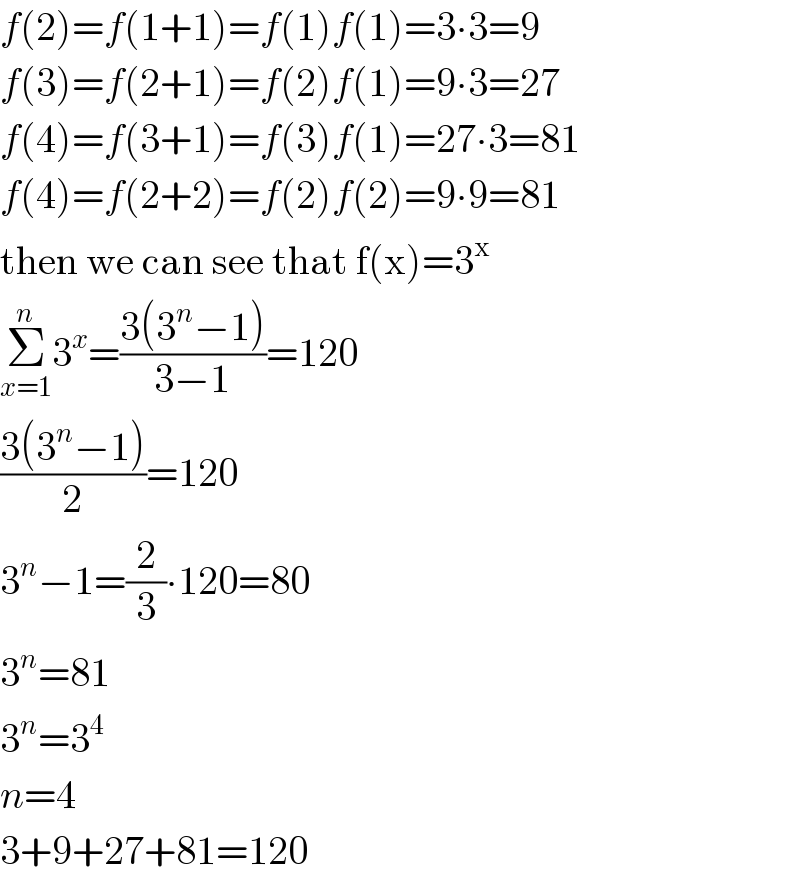
$${f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)={f}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}\right)={f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right){f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{3}\centerdot\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{9} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)={f}\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{1}\right)={f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right){f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{9}\centerdot\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{27} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{4}\right)={f}\left(\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{1}\right)={f}\left(\mathrm{3}\right){f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{27}\centerdot\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{81} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{4}\right)={f}\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2}\right)={f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right){f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{9}\centerdot\mathrm{9}=\mathrm{81} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{see}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{3}^{{x}} =\frac{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{3}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{120} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{3}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{120} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\centerdot\mathrm{120}=\mathrm{80} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}^{{n}} =\mathrm{81} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}^{{n}} =\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{9}+\mathrm{27}+\mathrm{81}=\mathrm{120} \\ $$
