Question Number 66245 by aliesam last updated on 11/Aug/19
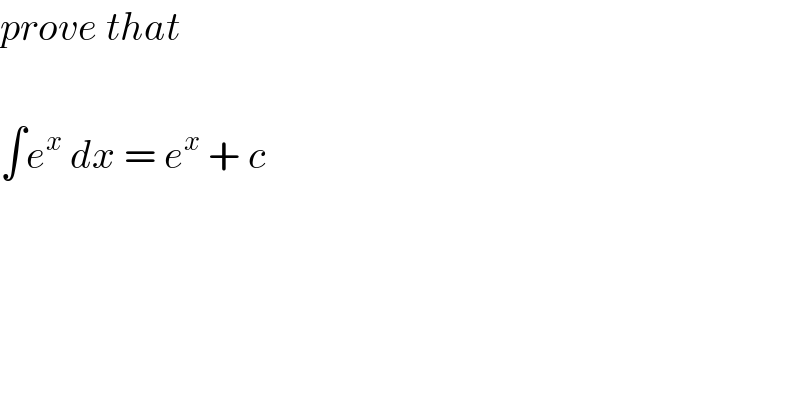
$${prove}\:{that} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\int{e}^{{x}} \:{dx}\:=\:{e}^{{x}} \:+\:{c} \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 11/Aug/19

$${let}\:\:{y}\:=\:{e}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:{e}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\int\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:\int{e}^{{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\:{y}\:=\:{e}^{{x}} \:+\:{c} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 11/Aug/19
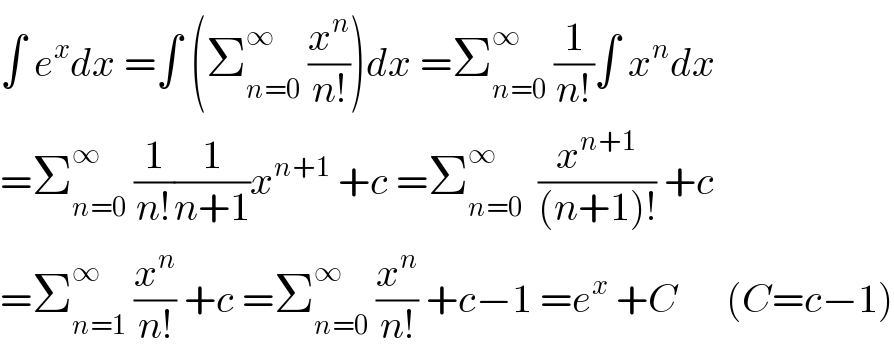
$$\int\:{e}^{{x}} {dx}\:=\int\:\left(\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\right){dx}\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}!}\int\:{x}^{{n}} {dx} \\ $$$$=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}!}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}+\mathrm{1}}{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:+{c}\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)!}\:+{c} \\ $$$$=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\:+{c}\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\:+{c}−\mathrm{1}\:={e}^{{x}} \:+{C}\:\:\:\:\:\:\left({C}={c}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 12/Aug/19
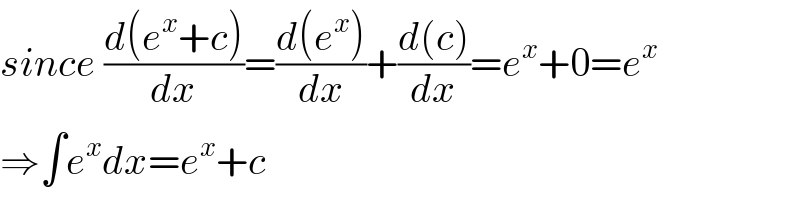
$${since}\:\frac{{d}\left({e}^{{x}} +{c}\right)}{{dx}}=\frac{{d}\left({e}^{{x}} \right)}{{dx}}+\frac{{d}\left({c}\right)}{{dx}}={e}^{{x}} +\mathrm{0}={e}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\int{e}^{{x}} {dx}={e}^{{x}} +{c} \\ $$
