Question Number 68642 by Maclaurin Stickker last updated on 14/Sep/19

$$\mathrm{Young}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{modulus}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{material}\:\mathrm{measures} \\ $$$$\mathrm{its}\:\mathrm{resistance}\:\mathrm{caused}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{external}\:\mathrm{stresses}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{On}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{vertical}\:\mathrm{wall}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{solid}\:\mathrm{mass}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{specific} \\ $$$$\mathrm{mass}\:\rho\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{Young}\:\varepsilon\:\mathrm{modulus}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{straight} \\ $$$$\mathrm{parallelepiped}\:\mathrm{shape},\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{dimensions} \\ $$$$\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{shown}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{figure}.\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{Based}\:\mathrm{on}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{correlations}\:\mathrm{between}\:\mathrm{physical} \\ $$$$\mathrm{quantities},\:\mathrm{determine}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{expression}\:\mathrm{that} \\ $$$$\mathrm{best}\:\mathrm{represents}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{deflection}\:\mathrm{suffered} \\ $$$$\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{solid}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{action}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{its}\:\mathrm{own}\:\mathrm{weight}. \\ $$
Commented by Maclaurin Stickker last updated on 14/Sep/19
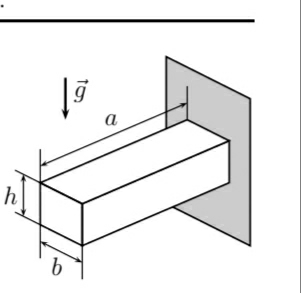
Commented by mr W last updated on 14/Sep/19
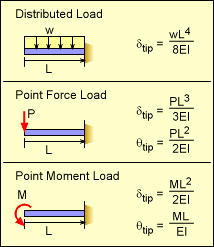
Commented by mr W last updated on 14/Sep/19

$$\delta=\frac{{wL}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{8}{EI}} \\ $$$${L}={a} \\ $$$${E}=\epsilon \\ $$$${I}=\frac{{bh}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$$${w}={bh}\rho{g} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{deflection}\:\delta=\frac{{bh}\rho{ga}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{8}\epsilon\frac{{bh}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{12}}}=\frac{\mathrm{3}\rho{ga}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{2}\epsilon{h}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
